Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome (ODDD) is a rare genetic condition that presents a unique set of challenges for those affected. With its distinct combination of ocular, dental, and digital abnormalities, ODDD is not only complex but also often misunderstood. Understanding this syndrome requires an exploration into its genetic roots, clinical manifestations, and management options.
This blog post aims to shed light on the intricacies of ODDD. From the underlying mutations in genes to the various physical traits associated with the syndrome, we will cover all aspects necessary for patients, families, and healthcare providers alike. Whether you’re seeking information out of personal interest or for medical purposes, this comprehensive overview serves as your guide through the multifaceted world of Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome.
Understanding Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia (ODDD): An Overview
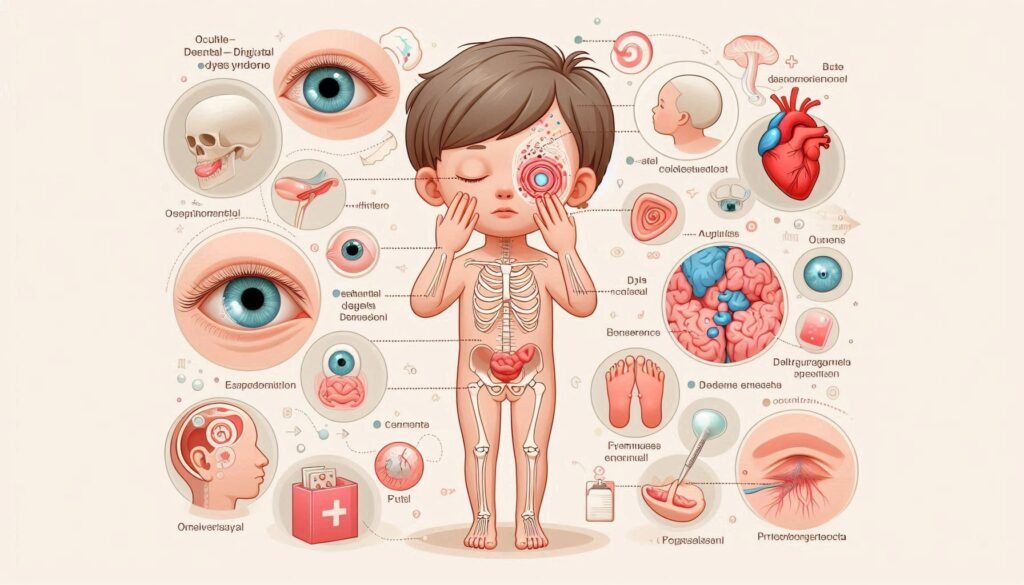
Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia (ODDD) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a spectrum of abnormalities affecting the eyes, teeth, and digits. This syndrome primarily results from mutations in the GJA1 gene, which encodes connexin 43—an essential protein for cell communication.
Individuals with ODDD may experience various clinical features that can significantly impact their daily lives. These include ocular issues such as cataracts or retinal problems, dental malformations like missing teeth or enamel defects, and digital anomalies encompassing shortening or duplication of fingers and toes.
“What Triggers Weber-Christian Disease Syndrome?”
The prevalence of ODDD is low, making it crucial for healthcare providers to recognize its signs early. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and improved quality of care for affected individuals.
Genetic Basis: Mutations in the GJA1 Gene
Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome (ODDD) is closely linked to mutations in the GJA1 gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein known as connexin 43, which plays a vital role in cell communication.
Mutations within the GJA1 gene disrupt the normal function of gap junctions. These gaps allow cells to share ions and small molecules, essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis. When these functions are impaired, various developmental abnormalities can arise.
“Why Does X-linked Agammaglobulinemia Affect Immunity?”
The genetic variability associated with ODDD illustrates how specific changes at the molecular level contribute to its diverse clinical manifestations. Understanding this genetic basis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted interventions.
Inheritance Patterns and Genetic Counseling
Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. This means that only one copy of the mutated gene from a parent can lead to the condition in offspring. Each child of an affected individual has a 50% chance of inheriting the syndrome.
“How Does X-linked Ichthyosis Syndrome Affect Skin?”
Genetic counseling plays a crucial role for families impacted by ODDD. It provides essential information about risks, testing options, and potential outcomes. Counselors help navigate complex emotional and medical decisions regarding family planning.
For those considering pregnancy, prenatal genetic testing is available. This offers insights into whether the fetus may inherit ODDD or if alternative reproductive options are advisable. Understanding inheritance patterns empowers families with knowledge and support during their journey.
Pathophysiology: Connexin 43 and Gap Junction Dysfunction
Connexin 43, a key protein in gap junctions, plays a crucial role in cellular communication. These channels allow the passage of ions and small molecules between adjacent cells, essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis.
“What Causes X-linked Lymphoproliferative Syndrome?”
In Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome (ODDD), mutations in the GJA1 gene disrupt connexin 43 function. This dysfunction can lead to impaired intercellular signaling, affecting various tissues throughout the body.
As a result, patients may experience diverse clinical manifestations. The impact on ocular health, dental development, and digital formation stems from this fundamental breakdown in cell-to-cell communication within critical systems. Understanding this pathophysiology is vital for developing targeted interventions.
Clinical Features: Ocular Manifestations
Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome is characterized by various ocular manifestations. Individuals with ODDD often experience anomalies such as colobomas, which are gaps in the eye structure. These can affect vision and overall eye health.
Other common features include cataracts and retinal detachment, leading to significant visual impairment if not addressed promptly. Dry eye syndrome may also occur due to inadequate tear production.
“Why Does X-linked Hypophosphatemia Affect Bones?”
Additionally, strabismus or misalignment of the eyes is frequently observed, impacting depth perception and coordination. Regular ophthalmologic evaluations are crucial for managing these complications effectively and preserving vision in affected individuals.
Dental Abnormalities in ODDD Syndrome
Dental abnormalities are a hallmark of Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome, significantly impacting individuals’ oral health. Patients often present with various dental anomalies, including hypodontia, which is the absence of one or more teeth.
“How Does X-linked Intellectual Disability Progress?”
Additionally, malformed teeth may occur, leading to issues such as malocclusion and impaired chewing function. These dental irregularities can also contribute to aesthetic concerns and reduced self-esteem.
Maintaining optimal oral hygiene becomes crucial for those affected by ODDD. Regular dental check-ups and tailored interventions play a vital role in managing these complications effectively while ensuring overall well-being in patients living with this syndrome.
Digital Malformations and Limb Involvement
Digital malformations are a hallmark of Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome. Individuals often experience various abnormalities in their fingers and toes, such as syndactyly or polydactyly. These conditions can significantly impact hand functionality.
“What Are The Signs of XMEA Syndrome?”
Limb involvement may vary widely among affected individuals. Some might have short or malformed digits, while others could present with more severe limb anomalies. This variability makes diagnosis challenging.
The genetic basis links these features to mutations in the GJA1 gene, affecting cellular communication and development during embryogenesis. As a result, these digital manifestations reflect broader underlying developmental issues associated with the syndrome.
Craniofacial Characteristics of ODDD
Individuals with Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome often exhibit distinct craniofacial features. These may include a prominent forehead, widely spaced eyes, and a flat nasal bridge. The facial appearance can vary significantly among affected individuals.
In addition to these primary characteristics, there may be anomalies in dental structure and alignment. Malocclusion and missing teeth are common findings. This can lead to further complications regarding oral health and aesthetics.
The shape of the head might also show irregularities such as brachycephaly or dolichocephaly. Such variations contribute to the unique presentation seen in those diagnosed with this syndrome, affecting both appearance and function throughout life.
Neurological Manifestations and Complications
Neurological manifestations in Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome can vary significantly among affected individuals. Some may experience developmental delays or cognitive impairments, affecting their daily functioning and learning abilities. Others might struggle with motor coordination due to central nervous system involvement.
Seizures are another potential complication linked to this syndrome, which can further complicate management and treatment strategies. Regular neurological evaluations are crucial for early detection and intervention.
Additionally, individuals with ODDD may face behavioral challenges stemming from both neurological issues and psychosocial stressors related to the syndrome’s physical manifestations. Addressing these concerns is vital for holistic care and support throughout their lives.
Diagnostic Criteria and Evaluation
Diagnosing Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome involves a thorough clinical evaluation complemented by genetic testing. Physicians typically assess the patient’s medical history and conduct physical examinations to identify characteristic features of the syndrome.
Diagnostic criteria include specific ocular, dental, and digital anomalies alongside craniofacial characteristics. Observing these traits helps healthcare providers establish an accurate diagnosis.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in confirming suspected cases by identifying mutations in the GJA1 gene. This molecular approach not only supports diagnosis but also aids in understanding inheritance patterns for family members at risk of carrying the mutation.
Genetic Testing and Molecular Diagnosis
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome. It primarily focuses on identifying mutations in the GJA1 gene, which is responsible for encoding Connexin 43. Testing can confirm a suspected diagnosis based on clinical features.
Molecular diagnosis typically involves techniques such as sequencing and deletion analysis. These tests help pinpoint specific genetic abnormalities associated with ODDD. Early detection through genetic testing aids in personalized management strategies.
Additionally, families may benefit from counseling regarding inheritance patterns and potential risks to future generations. Understanding these factors can empower families as they navigate the complexities of this rare syndrome while making informed medical decisions.
Differential Diagnosis: Similar Syndromes and Conditions
Differential diagnosis is crucial in identifying Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome. Several syndromes may present similar features, complicating the diagnostic process. Conditions such as Ectodermal Dysplasias and Nail-Patella Syndrome share overlapping symptoms, including dental anomalies and limb deformities.
Additionally, other genetic syndromes like Apert Syndrome or Crouzon Syndrome can display craniofacial characteristics that resemble those of ODDD. The presence of ocular abnormalities adds another layer to consider in these cases.
A thorough clinical evaluation combined with family history analysis is essential for accurate differentiation. Genetic testing can help clarify diagnoses when faced with challenging presentations involving multiple systems.
Management of Ocular Complications
Ocular complications in Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome often require specialized management. Regular ophthalmologic evaluations are essential to monitor for conditions such as cataracts, corneal opacities, and retinal issues. Early detection can significantly improve outcomes.
Treatment options may include corrective surgeries or interventions to address specific eye problems. For example, surgical procedures may help manage cataracts or align misaligned eyes effectively.
In addition to surgical options, visual aids like glasses or contact lenses can enhance vision quality. Supportive therapies also play a crucial role in helping patients adapt to their ocular challenges while maintaining independence and a better quality of life.
Dental Care and Interventions
Dental care for individuals with Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome requires special attention. These patients often exhibit various dental abnormalities, including missing teeth, malformed structures, and delayed eruption. Regular dental check-ups are essential to monitor these issues.
Interventions may include orthodontic treatments to correct misalignments and restorations for cavities or structural defects. Customized dental plans can help address individual needs effectively.
Collaboration between dentists, geneticists, and other healthcare providers is crucial in managing the oral health of patients with this syndrome. Such teamwork ensures comprehensive care that focuses on both functional and aesthetic outcomes while minimizing discomfort during procedures.
Orthopedic Considerations and Treatments
Orthopedic considerations in Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome (ODDD) often focus on limb malformations and joint issues. Patients may present with syndactyly, polydactyly, or other digital abnormalities that can affect mobility and function. Early evaluation of these conditions is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes.
Treatment typically includes corrective surgeries to improve alignment and enhance functionality of the limbs. Physical therapy plays a vital role in rehabilitation, helping patients regain strength and flexibility after surgical interventions.
It’s essential to monitor growth patterns as orthopedic complications can arise over time. Regular follow-ups with orthopedic specialists ensure timely interventions if new issues develop as the patient matures.
Neurological Management in ODDD
Neurological management in Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome focuses on addressing the diverse neurological manifestations that may arise. Patients can experience a range of issues, including developmental delays and seizure disorders. Early intervention is crucial for improving long-term outcomes.
A multidisciplinary team approach often involves neurologists, occupational therapists, and speech-language pathologists. These professionals work together to create individualized care plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Regular monitoring is essential to adapt treatment strategies as the patient grows. This includes assessing cognitive function and motor skills periodically, ensuring timely interventions are implemented when necessary. Comprehensive care promotes better quality of life for those affected by ODDD syndrome.
Multidisciplinary Care Approach
A multidisciplinary care approach is essential for individuals with Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome. This method involves collaboration between various healthcare professionals, including geneticists, ophthalmologists, dentists, orthopedic surgeons, and neurologists. Each specialist brings unique expertise to address the diverse needs of affected patients.
Effective communication among these professionals ensures a holistic treatment plan tailored to each individual’s symptoms and challenges. Regular meetings facilitate shared insights that lead to better patient outcomes.
Family involvement is also crucial in this model. Support from caregivers helps reinforce treatment plans at home while providing emotional support during medical visits. By working together, the team can enhance the overall quality of life for those living with ODDD syndrome.
Prognosis and Long-term Outcomes
The prognosis for individuals with Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome varies widely. Factors such as the severity of symptoms and associated complications significantly influence long-term outcomes. Many patients experience manageable symptoms, allowing them to lead fulfilling lives.
However, some may encounter more severe manifestations that can impact daily functioning and overall quality of life. Regular monitoring is essential to address issues as they arise.
With advances in medical care and a multidisciplinary approach, many individuals achieve better health outcomes. Early intervention strategies play a critical role in enhancing mobility, vision, and dental function while supporting psychosocial well-being throughout their journey.
Quality of Life and Psychosocial Support
Quality of life for individuals with Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome can be significantly impacted by their physical symptoms. These challenges often lead to social isolation and emotional distress, making psychosocial support crucial.
Access to counseling services can help patients and families navigate the emotional complexities associated with the syndrome. Support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, fostering connections, and reducing feelings of loneliness.
Education about ODDD can empower both patients and caregivers. Understanding the condition helps them advocate for necessary accommodations in school or work settings, enhancing overall quality of life while promoting resilience within the community.
Research Advancements and Future Therapeutic Prospects
Research into Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Syndrome (ODDD) has gained momentum in recent years. Scientists are exploring novel therapies that target the underlying genetic mutations associated with this condition. Advances in gene therapy hold promise for correcting or mitigating the effects of GJA1 gene mutations.
Additionally, researchers are investigating potential pharmacological interventions to manage symptoms more effectively. Clinical trials are underway to assess new treatment modalities that could enhance patient outcomes.
The integration of innovative technologies, such as CRISPR gene editing, offers exciting prospects for future therapeutic options. As our understanding of ODDD deepens through ongoing research, there is hope for improved management strategies and possibly a cure down the line. This evolving landscape provides encouragement not only for patients but also for their families and healthcare providers involved in care and support.