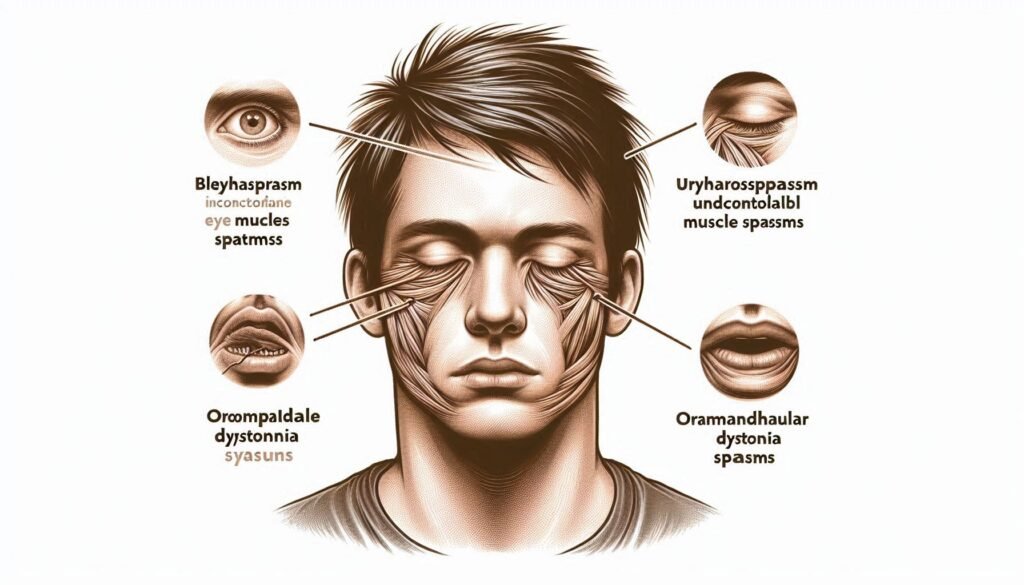
Meige Syndrome is a little-known yet complex disorder that significantly affects the lives of those who experience it. Characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, this focal dystonia can lead to troubling symptoms such as blepharospasm and oromandibular dystonia. Despite its challenges, understanding Meige Syndrome is crucial for both patients and caregivers alike.
In this blog post, we will explore its historical roots, clinical features, diagnostic criteria, and treatment options available today. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of this fascinating condition and uncover valuable insights for managing life with Meige Syndrome effectively.
Meige Syndrome: A Complex Focal Dystonia Disorder
Meige Syndrome is classified as a complex focal dystonia disorder, primarily affecting the muscles of the face and jaw. This neurological condition involves involuntary movements that can lead to significant discomfort and disruption in daily life.
Individuals with Meige often experience blepharospasm, which causes uncontrollable blinking or eye closure, alongside oromandibular dystonia, resulting in abnormal contractions of facial muscles. These symptoms may worsen over time if left untreated.
“How Does Sleep Apnea Syndrome Affect Your Health?”
The interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors contributes to its development. While it can occur at any age, onset typically happens in middle adulthood. Awareness and understanding are key components for those affected by this challenging syndrome.
Historical Perspective: Henry Meige and the Syndrome’s Description
Henry Meige was a pioneering French neurologist in the early 20th century who made significant contributions to our understanding of dystonia. In 1910, he first described what is now known as Meige Syndrome. His observations were detailed and nuanced, focusing on the involuntary movements affecting the face and jaw.
Meige noted that these movements could be socially debilitating for patients. He highlighted how they often led to discomfort during communication and eating. His work laid crucial groundwork for further research into focal dystonias.
“What Causes Oculocerebrorenal Syndrome? Expert Guide”
Despite being initially met with skepticism, his findings gradually gained acceptance within the medical community. Today, Meige’s name remains synonymous with this complex disorder, reflecting his lasting impact on neurology and patient care.
Pathophysiology: Basal Ganglia Dysfunction and Neurotransmitter Imbalance
Meige Syndrome is primarily associated with dysfunction in the basal ganglia, a group of nuclei that play an essential role in regulating movement. The basal ganglia help control voluntary motor function and are crucial for smooth and coordinated movements. When these structures malfunction, it can lead to involuntary muscle contractions.
Neurotransmitter imbalances also significantly contribute to Meige Syndrome. Dopamine, acetylcholine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) interact intricately within the brain’s circuitry. An imbalance among these neurotransmitters may result in abnormal signaling pathways that trigger dystonic symptoms.
“Why Does Oculo-Dento-Digital Dysplasia Affect Multiple Systems?”
Understanding this complex interplay helps researchers develop targeted therapies aimed at restoring balance within these critical neural circuits. Continued research into neurotransmitter dynamics remains vital for devising effective treatment strategies for individuals living with Meige Syndrome.
Clinical Features: Blepharospasm and Oromandibular Dystonia
Blepharospasm is one of the hallmark features of Meige Syndrome. It involves involuntary blinking and eyelid spasms, which can significantly impair vision. Patients may experience discomfort or a sensation of irritation in the eyes, often leading to fatigue and anxiety.
Oromandibular dystonia is another key clinical aspect. This condition affects the muscles of the jaw, tongue, and lower face. Individuals may find it difficult to chew or speak due to painful muscle contractions.
“How Does Ochoa Syndrome Impact Bladder Function?”
Together, these symptoms create a complex challenge for those affected by Meige Syndrome. The interactions between eye movements and oral function can lead to social withdrawal and impact overall quality of life.
Diagnostic Criteria: Differentiating Meige from Other Dystonias
Diagnosing Meige Syndrome requires a thorough assessment to distinguish it from other forms of dystonia. Key symptoms include blepharospasm, characterized by involuntary eyelid closure, and oromandibular dystonia affecting the jaw and mouth muscles.
Clinicians often utilize specific diagnostic criteria based on symptom onset, duration, and response to treatment. These details help differentiate Meige from conditions like cervical dystonia or task-specific dystonias.
“What Are The Signs of Oculocutaneous Albinism Syndrome?”
A comprehensive neurological examination is essential for an accurate diagnosis. This may involve observing muscle contractions during various activities while ruling out secondary causes such as medication side effects or other neurological disorders.
Triggers and Exacerbating Factors in Meige Syndrome
Meige syndrome can be influenced by various triggers and exacerbating factors. Stress is a significant contributor, often leading to increased muscle tension and involuntary movements. Situations that provoke anxiety or emotional distress may worsen symptoms.
Environmental factors also play a role. Bright lights, loud noises, and certain visual stimuli can trigger episodes of blepharospasm or oromandibular dystonia in affected individuals. These sensory inputs can overwhelm the nervous system, resulting in heightened reactions.
“Why Does Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum Affect Development?”
Additionally, fatigue has been linked to symptom exacerbation. Lack of sleep or physical exhaustion may lower resilience against involuntary movements. Recognizing these triggers is essential for managing Meige syndrome effectively and improving daily functioning.
Neuroimaging Findings: Insights from Functional and Structural Studies
Neuroimaging has provided significant insights into Meige Syndrome. Functional MRI (fMRI) studies show altered brain activity in individuals with this disorder, particularly within the basal ganglia and related networks. These changes help us understand the underlying mechanisms of dystonia.
Structural imaging techniques like MRI reveal abnormalities in specific brain regions associated with motor control. These findings suggest that structural differences may contribute to the manifestation of symptoms such as blepharospasm and oromandibular dystonia.
Recent advancements in neuroimaging allow researchers to better visualize these anomalies. Understanding these patterns not only aids diagnosis but also enhances our comprehension of potential therapeutic targets for managing Meige Syndrome effectively.
Genetic Factors: Current Understanding and Ongoing Research
Research into the genetic factors of Meige Syndrome is still in its infancy. Current studies suggest a potential hereditary component, but specific genes remain unidentified. Understanding these genetic underpinnings could offer insights into susceptibility and disease progression.
Researchers are exploring gene variants associated with dystonia disorders to determine whether similar patterns exist in Meige Syndrome. The complexity of this disorder makes it challenging to pinpoint exact genetic markers.
Ongoing research aims to unravel the intricate relationship between genetics and environmental influences that may trigger or exacerbate symptoms. As technology advances, more precise investigations are expected to emerge, offering hope for improved diagnostics and personalized treatment options for those affected by Meige Syndrome.
Treatment Approaches: Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions play a crucial role in managing Meige Syndrome. Medications such as anticholinergics are often the first line of treatment. They help reduce muscle spasms and improve control over involuntary movements.
Benzodiazepines can also be prescribed to alleviate anxiety, which may exacerbate symptoms. These medications promote relaxation and may provide temporary relief from dystonic episodes.
Additionally, dopaminergic agents have shown effectiveness in some patients by addressing neurotransmitter imbalances associated with this condition. However, finding the right medication or combination can be a trial-and-error process tailored to each individual’s needs. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure optimal management of symptoms while minimizing side effects.
Botulinum Toxin Therapy: Techniques and Efficacy in Meige Syndrome
Botulinum toxin therapy is a primary treatment for Meige Syndrome, providing significant relief from symptoms. It works by blocking the release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions, reducing involuntary muscle contractions.
The injection technique involves targeting specific muscles affected by blepharospasm and oromandibular dystonia. Physicians often use electromyography to enhance precision during administration, ensuring optimal outcomes.
Patients typically experience improvement within weeks of the injections, with effects lasting three to six months. While most tolerate the procedure well, some may encounter side effects like temporary eyelid drooping or dry mouth. Regular follow-ups are crucial for adjusting doses and monitoring efficacy over time.
Deep Brain Stimulation: A Surgical Option for Refractory Cases
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) has emerged as a promising surgical option for patients with Meige Syndrome who do not respond to conventional treatments. This procedure involves the implantation of electrodes in specific brain regions, delivering electrical impulses that help regulate abnormal neural activity.
The targeted areas often include the globus pallidus internus or subthalamic nucleus. By modulating these pathways, DBS can alleviate symptoms associated with blepharospasm and oromandibular dystonia effectively.
Patients undergoing DBS typically experience significant improvements in motor function and quality of life. However, careful patient selection is crucial, as it requires thorough evaluation by specialists familiar with both Meige Syndrome and movement disorders.
Complementary Therapies: Role of Physical and Occupational Therapy
Complementary therapies, such as physical and occupational therapy, play a vital role in managing Meige Syndrome. These approaches focus on improving muscle control and coordination. They help patients regain some degree of voluntary movement.
Physical therapy often involves exercises that enhance strength and flexibility. This can alleviate the tension caused by involuntary muscle contractions associated with dystonia. Tailored programs aim to address individual needs, allowing for gradual progress over time.
Occupational therapy emphasizes adapting daily activities to reduce strain and improve quality of life. Therapists provide strategies for overcoming challenges like speech difficulties or impaired movements during eating. Together, these therapies create a holistic treatment plan that addresses both physical symptoms and functional limitations.
Psychological Impact: Coping with Visible Facial Movements
Living with Meige Syndrome can significantly affect a person’s mental health. The involuntary facial movements often lead to anxiety and self-consciousness. Many individuals find themselves avoiding social situations, fearing judgment or misunderstanding.
Coping strategies play a crucial role in managing these feelings. Support groups offer connection and understanding from others facing similar challenges. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can also help address negative thought patterns associated with visible symptoms.
Additionally, mindfulness techniques promote acceptance of the condition and reduce stress levels. Engaging in activities that build confidence, such as art or performance, can provide an outlet for emotions while fostering resilience against societal pressures related to appearance.
Quality of Life Considerations in Meige Syndrome
Individuals with Meige Syndrome often face significant challenges that impact their quality of life. The involuntary facial movements can lead to social anxiety and isolation, as many feel self-conscious in public settings. This emotional strain can exacerbate the physical symptoms.
Daily activities like eating, speaking, or even maintaining eye contact become more difficult. These disruptions not only affect personal interactions but also professional life, leading to potential career limitations and financial stress.
Support systems play a crucial role in enhancing well-being for those affected by Meige Syndrome. Access to therapy groups and resources helps individuals share experiences and coping strategies while fostering a sense of community that alleviates feelings of loneliness.
Speech and Swallowing Difficulties: Assessment and Management
Individuals with Meige Syndrome may experience significant speech and swallowing difficulties. The involuntary muscle contractions can affect the muscles involved in articulation, leading to slurred or unclear speech. This can hinder effective communication and contribute to social withdrawal.
Assessment of these difficulties typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a speech-language pathologist. They will assess articulatory precision, voice quality, and overall swallowing function. Specialized tests may be utilized to determine the severity of dysphagia.
Management strategies often include tailored speech therapy programs focused on improving clarity and fluidity of speech. Swallowing techniques are also taught to enhance safety during eating and drinking, ensuring individuals maintain adequate nutrition while minimizing risks.
Ocular Complications: Dry Eye and Vision Impairment
Individuals with Meige Syndrome may experience ocular complications, including dry eye and vision impairment. These issues arise due to involuntary eyelid spasms, which can disrupt normal blinking patterns. As a result, the eyes may not receive adequate lubrication.
Dry eye can lead to discomfort, redness, and increased sensitivity to light. Patients often report a gritty sensation that affects daily activities like reading or using screens. Regular use of artificial tears is commonly recommended for relief.
Vision impairment in Meige Syndrome occurs when prolonged muscle contractions interfere with visual focus. This makes it challenging for individuals to maintain clear sight during tasks requiring concentration. Addressing these ocular symptoms is essential for improving quality of life and overall well-being.
Latest Research: Novel Treatment Modalities and Clinical Trials
Recent advancements in Meige Syndrome research have led to the exploration of innovative treatment modalities. Clinical trials are investigating new pharmacological agents that target specific neurotransmitter pathways involved in dystonia. These studies aim to improve efficacy and reduce side effects associated with current treatments.
Additionally, researchers are evaluating gene therapy approaches that may offer a long-term solution by addressing the underlying genetic factors contributing to Meige Syndrome. Preliminary results indicate promising outcomes, although further investigation is needed.
Moreover, multidisciplinary approaches involving neurorehabilitation techniques show potential for enhancing overall quality of life. Efforts focus on integrating physical therapy with traditional medical treatments to optimize patient care and functional abilities in individuals living with this condition.
Living with Meige Syndrome: Daily Challenges and Adaptations
Living with Meige Syndrome presents unique challenges that require adaptations in daily life. Individuals often experience involuntary facial movements, which can impact social interactions and self-esteem. These symptoms may lead to avoidance of certain situations, creating feelings of isolation.
Adapting routines is essential. Many find it helpful to establish a consistent schedule, allowing for periods of rest. Support networks also play a crucial role; connecting with others who understand the condition can be empowering.
Practical strategies include using sunglasses or hats to minimize triggers from bright lights and stress management techniques such as mindfulness or relaxation exercises. Occupational therapy can provide tailored coping mechanisms specific to individual needs.
Navigating these complexities requires resilience and patience but finding effective ways to manage symptoms significantly enhances quality of life for those living with Meige Syndrome.