McCune-Albright Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that can significantly affect multiple systems within the body. With its unique features and complexities, understanding this syndrome is crucial for those living with it and their families. From bone abnormalities to hormonal imbalances, McCune-Albright presents an array of challenges.
This blog post delves into the genetics behind this fascinating condition, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management strategies. Whether you’re a patient seeking information or simply curious about this intriguing mosaic disorder, there’s plenty to discover here. Let’s embark on this informative journey together!
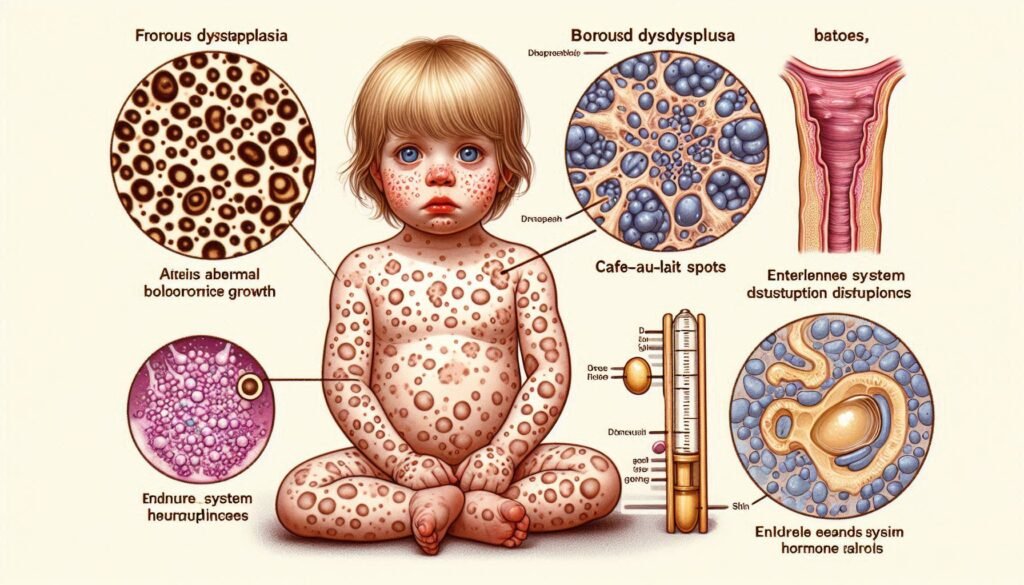
Genetic Mosaic Disorder: Understanding McCune-Albright Syndrome
McCune-Albright Syndrome is classified as a genetic mosaic disorder, meaning not all cells in the body carry the same genetic makeup. This results from mutations occurring after fertilization, leading to a mix of normal and affected cells.
The syndrome arises primarily due to mutations in the GNAS gene, which plays a key role in regulating signaling pathways for various hormones and growth factors. As these mutated cells proliferate, they can cause distinct clinical features associated with the condition.
“What Are The Signs of Parsonage-Turner Syndrome?”
Individuals may experience varying degrees of severity depending on how many cells are affected by the mutation. This variability makes each case unique and underscores the importance of personalized medical care for those diagnosed with McCune-Albright Syndrome.
GNAS Gene Mutations: The Molecular Basis of McCune-Albright
McCune-Albright Syndrome is primarily caused by mutations in the GNAS gene. This gene plays a crucial role in cell signaling pathways, particularly those involving hormones and growth factors. A mutation leads to abnormal protein production that affects various tissues.
These mutations are unique because they occur after fertilization, resulting in a mosaic pattern of affected cells throughout the body. This means that not every cell carries the mutation; rather, some do while others remain normal.
“Why Does Patterson-Kelly Syndrome Cause Swallowing Issues?”
The result is the characteristic features of McCune-Albright Syndrome, including fibrous dysplasia of bone and hormonal imbalances. Understanding these molecular mechanisms can help guide treatment options for individuals affected by this complex disorder.
Clinical Triad: Fibrous Dysplasia, Café-au-lait Spots, and Endocrine Dysfunction
McCune-Albright Syndrome is characterized by a clinical triad that includes fibrous dysplasia, café-au-lait spots, and endocrine dysfunction. Fibrous dysplasia leads to abnormal bone growth, resulting in weak and deformed bones. Patients may experience pain and increased fracture risk due to this condition.
Café-au-lait spots are flat, pigmented skin lesions that can appear anywhere on the body. These freckle-like marks tend to be lighter than typical moles and often increase with age. Their presence is an important diagnostic clue for McCune-Albright.
“How Does Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Syndrome Affect Myelin?”
Endocrine dysfunction occurs when hormone levels become imbalanced. This can lead to various complications such as precocious puberty or hyperfunction of certain glands like the thyroid or adrenal glands. Each component of this triad contributes significantly to patient management.
Skeletal Manifestations: Fibrous Dysplasia and Its Complications
Fibrous dysplasia is a key skeletal manifestation of McCune-Albright Syndrome. This condition occurs when normal bone is replaced by fibrous tissue, leading to weakened bones. It can affect any bone but commonly impacts the pelvis, skull, and long bones.
Complications arise from this abnormal growth. Patients may experience pain or deformities due to structural weaknesses in affected areas. These changes can lead to fractures and limit mobility.
“What Triggers Primary Raynaud’s Syndrome? Complete Guide”
In some cases, fibrous dysplasia may result in craniofacial abnormalities, impacting appearance and function. Monitoring through imaging studies helps assess the extent of these complications for better management strategies tailored to individual needs.
Endocrine Abnormalities: Precocious Puberty and Other Hormonal Disorders
Endocrine abnormalities are a hallmark of McCune-Albright Syndrome. One of the most notable issues is precocious puberty, which occurs when children experience early onset of secondary sexual characteristics. This can lead to physical and emotional challenges for affected individuals.
“How Does PTSD Affect Mental Health? Recovery Guide”
Additionally, patients may face other hormonal disorders such as hyperthyroidism or growth hormone excess. These conditions stem from excessive hormone production due to GNAS gene mutations affecting endocrine glands.
The management of these hormonal imbalances is crucial in improving quality of life. Regular monitoring and tailored treatment plans help mitigate complications associated with premature development and ensure balanced hormone levels in patients with McCune-Albright Syndrome.
Café-au-Lait Skin Pigmentation: Patterns and Significance
Café-au-lait spots are one of the hallmark features of McCune-Albright Syndrome. These flat, pigmented lesions can vary in size and typically present as light brown patches on the skin. Their name comes from their resemblance to coffee mixed with milk.
The presence of multiple café-au-lait spots often raises suspicion for genetic disorders. In McCune-Albright Syndrome, these spots result from mutations affecting melanin production. They usually appear during infancy or early childhood, serving as a key diagnostic indicator.
“What Is Qazi Syndrome? Understanding Rare Genetic Conditions”
Understanding the significance of these pigmentation patterns is crucial for medical professionals. The number and distribution can help differentiate McCune-Albright from other conditions that feature similar skin changes.
Diagnostic Approaches: Imaging Studies and Genetic Testing
Diagnosing McCune-Albright Syndrome involves a combination of imaging studies and genetic testing. X-rays are often the first step, revealing fibrous dysplasia in affected bones. CT scans or MRIs can provide detailed images, helping to assess any complications related to this skeletal abnormality.
Genetic testing is crucial for confirming the diagnosis. It focuses on identifying mutations in the GNAS gene, which plays a central role in this disorder’s development. A blood sample is typically required for analysis.
These diagnostic tools not only aid in confirming McCune-Albright Syndrome but also help monitor disease progression and guide treatment options effectively. Early detection can significantly impact patient management strategies moving forward.
Management of Fibrous Dysplasia: Surgical and Non-Surgical Options
Management of fibrous dysplasia involves both surgical and non-surgical approaches, tailored to the patient’s specific needs. Non-surgical options often include medication for pain management and monitoring the condition through regular imaging studies. These methods help track any changes in bone lesions.
When complications arise or if significant deformities develop, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery can involve curettage, which removes abnormal tissue, followed by grafting to restore normal bone structure. In more severe cases, orthopedic surgeries might be needed to correct skeletal abnormalities.
Multidisciplinary care is crucial for optimal outcomes. Collaboration among specialists ensures a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses all aspects of fibrous dysplasia while considering individual patient circumstances.
Endocrine Management: Treating Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances in McCune-Albright Syndrome often necessitate careful management. Patients may experience conditions like precocious puberty due to excess hormone production. Addressing this requires a tailored approach.
Treatment options include medications that can inhibit premature sexual development and manage other endocrine disorders. For instance, aromatase inhibitors are sometimes prescribed to slow down estrogen production in young girls experiencing early maturation.
Regular monitoring of hormonal levels is essential for effective management. Endocrinologists play a pivotal role, adjusting therapies as the patient grows and their needs change. This proactive care helps mitigate complications associated with hormonal imbalances while promoting overall health and well-being.
Precocious Puberty in McCune-Albright: Causes and Interventions
Precocious puberty is a notable aspect of McCune-Albright Syndrome, often occurring due to hormonal imbalances. The GNAS gene mutation leads to autonomous activation of hormone-producing glands. As a result, individuals may experience early onset of secondary sexual characteristics.
This condition can manifest in various ways. Girls might develop breast tissue and menstruation before age 9, while boys could show signs such as testicular enlargement or pubic hair growth earlier than expected. These changes can be distressing for both patients and families.
Interventions typically involve managing hormone levels through medications that inhibit premature development. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals ensures timely adjustments to treatment plans tailored specifically for the individual’s needs.
Bone Pain Management: Strategies and Considerations
Managing bone pain in McCune-Albright Syndrome requires a comprehensive approach. Pain can arise from fibrous dysplasia, which often affects the skeletal system. Understanding the source is crucial for effective treatment.
Medications like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics are commonly used to alleviate discomfort. Physical therapy can also be beneficial, helping strengthen muscles around affected bones and improving mobility.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct deformities or stabilize fractures. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals ensures that pain management strategies align with the patient’s evolving needs and overall health goals.
Orthopedic Complications: Fractures and Deformities
Individuals with McCune-Albright Syndrome often face orthopedic complications, particularly fractures and deformities. The presence of fibrous dysplasia weakens bone structure, making it more susceptible to breaks. These fractures can occur even with minimal trauma, leading to significant pain and mobility issues.
Deformities may also arise due to abnormal bone growth patterns associated with the syndrome. As bones develop unevenly, patients might experience limb length discrepancies or skeletal malformations. These changes can affect posture and gait.
Management of these orthopedic challenges is crucial for maintaining quality of life. Regular monitoring through imaging studies helps detect emerging issues early on, allowing for timely interventions that can mitigate further complications.
Quality of Life: Living with a Multisystem Disorder
Living with McCune-Albright Syndrome can present numerous challenges. Patients often face a range of symptoms that affect multiple systems in the body. This complexity can lead to physical discomfort and emotional strain.
Daily life may involve managing chronic pain, addressing hormonal imbalances, and dealing with skin pigmentation changes. These factors significantly impact social interactions, self-esteem, and overall mental health.
Support from family, friends, and healthcare providers is crucial for improving quality of life. Resources such as support groups can offer valuable connections to others facing similar challenges. With the right strategies in place, individuals can navigate their unique experiences while striving for fulfillment in daily activities.
Long-term Prognosis and Disease Progression
Long-term prognosis for individuals with McCune-Albright Syndrome varies widely. Some patients may experience mild symptoms that require minimal intervention, while others face significant challenges from multiple complications.
Disease progression can be unpredictable, often influenced by the specific mutations in the GNAS gene and individual health factors. Regular monitoring is essential to manage symptoms effectively.
As patients age, skeletal issues like fractures and deformities may arise, impacting mobility and quality of life. Endocrine abnormalities also necessitate ongoing assessment to address hormonal imbalances as they emerge throughout life.
Psychological Support for Patients and Families
Living with McCune-Albright Syndrome can be challenging for both patients and their families. The unpredictability of symptoms may lead to anxiety, stress, and emotional distress. Psychological support plays a vital role in coping with these challenges.
Counseling offers a safe space for individuals to express their feelings. It aids in understanding the complexities of the disorder while providing coping strategies. Family therapy can also foster communication and strengthen relationships.
Support groups create community among those affected by McCune-Albright Syndrome. Sharing experiences helps reduce feelings of isolation. These connections provide comfort as families navigate this multifaceted condition together.
Genetic Counseling: Implications for Family Planning
Genetic counseling plays a crucial role for families affected by McCune-Albright Syndrome. It provides valuable insights into the nature of this genetic mosaic disorder and its inheritance patterns. Understanding these aspects helps families make informed decisions regarding family planning.
Counselors assess risks based on family history and specific gene mutations, particularly in the GNAS gene. They can guide prospective parents on the likelihood of passing this condition to their children. This knowledge is empowering, allowing individuals to explore reproductive options.
Additionally, support networks formed through genetic counseling can be invaluable. Families often find comfort in connecting with others who share similar experiences and challenges related to McCune-Albright Syndrome.
Latest Research: Targeted Therapies and Clinical Trials
Recent advancements in McCune-Albright Syndrome research have opened avenues for targeted therapies. Scientists are investigating the role of GNAS gene mutations and how they contribute to disease manifestations. This understanding is crucial for developing effective treatments.
Clinical trials are currently underway, focusing on novel approaches to manage symptoms associated with fibrous dysplasia and hormonal imbalances. These studies aim to provide insights into personalized medicine strategies that could improve patient outcomes significantly.
Moreover, researchers are exploring the potential of drugs that inhibit specific signaling pathways activated by GNAS mutations. Such targeted interventions may help mitigate complications and enhance the quality of life for those living with this complex disorder.
Multidisciplinary Care Approach for McCune-Albright Patients
A multidisciplinary care approach is essential for managing McCune-Albright syndrome effectively. Patients often present with a variety of symptoms that require input from different specialists. This team may include endocrinologists, orthopedic surgeons, dermatologists, and geneticists.
Each specialist contributes unique expertise to address the complex needs of patients. For example, while endocrinologists focus on hormonal imbalances like precocious puberty, orthopedic surgeons manage complications related to fibrous dysplasia.
Coordinated care ensures comprehensive treatment plans tailored to individual patients. Regular communication among specialists helps streamline management strategies and improves patient outcomes significantly.
Transitioning from Pediatric to Adult Care
Transitioning from pediatric to adult care is a significant step for individuals with McCune-Albright Syndrome. This process often begins in the late teen years, as patients start taking more responsibility for their health management.
Adult healthcare providers may not be familiar with this rare condition, making it essential to prepare and educate them about specific needs. Continuous collaboration between pediatricians and adult specialists can facilitate smoother transitions.
Education on self-management of symptoms and understanding potential complications is vital. Patients should also be informed about available support groups that connect them with others facing similar challenges.
Maintaining regular check-ups will help monitor long-term outcomes and adjust treatments as necessary. Careful planning ensures that individuals affected by McCune-Albright Syndrome can lead fulfilling lives while managing their health effectively.


