Holt-Oram Syndrome is a fascinating yet complex genetic condition often referred to as Heart-Hand Syndrome. It presents unique challenges and features that affect both the heart and upper limbs of those affected. Understanding this syndrome can empower families, health professionals, and individuals living with it.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Holt-Oram Syndrome, exploring its genetic underpinnings, clinical manifestations, management strategies, and much more. Whether you’re seeking knowledge for yourself or a loved one, this resource aims to provide clarity on what you need to know about this rare condition. Join us as we uncover the essential aspects of Holt-Oram Syndrome!
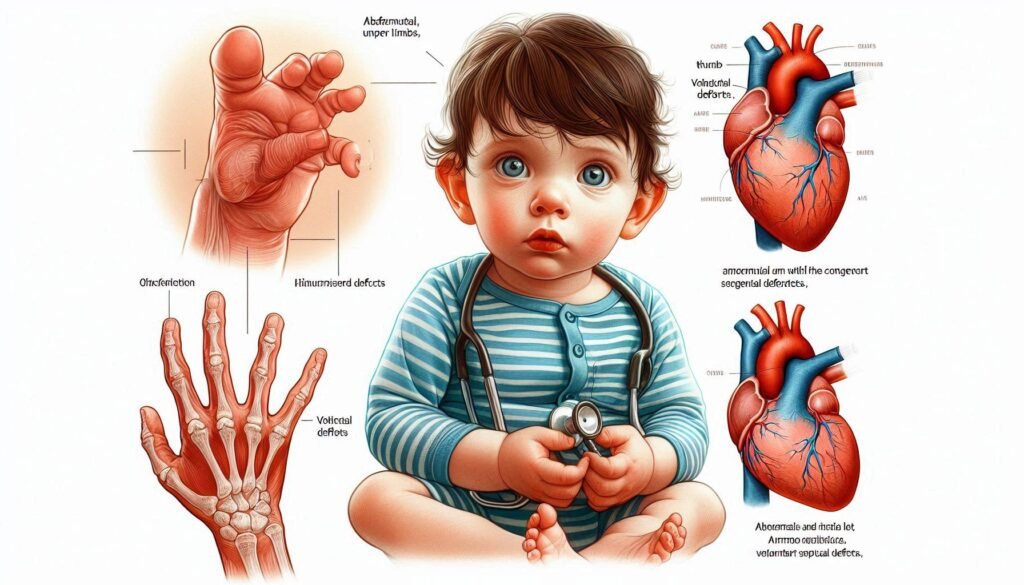
Holt-Oram Syndrome overview: The Heart-Hand Syndrome
Holt-Oram Syndrome, commonly known as Heart-Hand Syndrome, is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the heart and upper limbs. It was first described by Dr. Holt and Dr. Oram in 1960 and is characterized by congenital heart defects alongside skeletal abnormalities in the arms.
“How Does Weaver Syndrome Impact Growth?”
Individuals with this syndrome often exhibit variations in limb development, such as missing or shortened bones in the forearms and hands. The severity of these physical manifestations can vary widely among affected individuals.
Heart-related issues frequently associated with Holt-Oram Syndrome include atrial septal defects and ventricular septal defects. Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in managing these conditions effectively to improve quality of life for those impacted.
Genetic Basis: TBX5 Gene Mutations
Holt-Oram Syndrome is primarily caused by mutations in the TBX5 gene. This gene plays a crucial role in the development of the heart and upper limbs during embryonic growth.
When mutations occur, they disrupt normal cardiac and skeletal formation, leading to characteristic features associated with this syndrome. These genetic alterations can vary significantly among individuals affected by Holt-Oram Syndrome.
“What Causes Williams Syndrome? Complete Guide”
TBX5 gene mutations are often inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can lead to transmission of the condition to offspring. Genetic testing can confirm these mutations, guiding diagnosis and management strategies for patients.
Inheritance Patterns and Genetic Counseling
Holt-Oram Syndrome follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. This means that one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can lead to the syndrome in their child. Each child has a 50% chance of inheriting the condition.
“Why Does WAGR Syndrome Affect Multiple Systems?”
Genetic counseling plays a crucial role for families impacted by Holt-Oram Syndrome. It provides essential information about the risks and implications of passing on genetic traits. Counselors help parents understand testing options and potential outcomes.
Understanding family history is vital when assessing risk factors. Parents with known cases or those who have had children with Holt-Oram should seek genetic advice before conception, ensuring informed decisions about future pregnancies.
Prevalence and Epidemiology of Holt-Oram Syndrome
Holt-Oram Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder, affecting approximately 1 in 100,000 individuals. Its incidence can vary based on geographic and ethnic factors.
This syndrome occurs equally among genders but shows variability in expressivity. Some families may experience multiple affected members while others have isolated cases.
“How Does Warfarin Embryopathy Syndrome Develop?”
Due to its association with heart and upper limb abnormalities, many diagnoses arise during infancy or early childhood. Awareness of Holt-Oram Syndrome remains crucial for timely intervention and management strategies that enhance quality of life for those affected.
Clinical Features: Cardiac Manifestations
Holt-Oram Syndrome is characterized by significant cardiac manifestations, primarily affecting the structure of the heart. Patients often present with congenital heart defects, including atrial septal defects and ventricular septal defects. These abnormalities can lead to complications if left untreated.
“What Triggers Weber-Christian Disease Syndrome?”
Arrhythmias are also common in individuals with Holt-Oram Syndrome due to structural changes in the heart’s electrical system. This can result in irregular heartbeats that may require monitoring or intervention.
Additionally, some patients experience more severe conditions like tetralogy of Fallot or transposition of great vessels. Early detection through routine evaluations is crucial for managing these potentially life-threatening issues effectively.
Upper Limb Abnormalities in Holt-Oram Syndrome
Individuals with Holt-Oram Syndrome often exhibit upper limb abnormalities, which can vary significantly in severity and presentation. Common features include hypoplasia or absence of the radius, leading to shortened forearms. This can affect hand function and dexterity.
“Why Does X-linked Agammaglobulinemia Affect Immunity?”
Other malformations may involve underdeveloped thumbs or fingers, making daily activities challenging. Some individuals may have complete syndactyly, where fingers are fused together.
These variations impact not just physical appearance but also functional capabilities. Early intervention through therapy and orthopedic care is crucial to enhance mobility and independence in affected individuals. Tailored treatment plans help address specific needs associated with these upper limb anomalies.
Skeletal Involvement Beyond the Upper Limbs
Holt-Oram Syndrome primarily affects the heart and upper limbs, but skeletal involvement can extend beyond these areas. Some patients may exhibit vertebral anomalies, including scoliosis or kyphosis. These conditions can contribute to discomfort and functional limitations.
“How Does X-linked Ichthyosis Syndrome Affect Skin?”
In addition to spinal issues, individuals might experience abnormalities in the ribs and pelvis. These variations could lead to a range of complications that impact mobility and overall health.
Understanding these broader skeletal involvements is crucial for comprehensive care. Early identification allows for timely interventions tailored to each patient’s unique needs. This proactive approach helps improve quality of life by addressing both cardiac and skeletal challenges associated with Holt-Oram Syndrome.
Diagnostic Criteria and Evaluation
Diagnosing Holt-Oram Syndrome involves a thorough clinical evaluation. Health professionals typically look for specific physical signs and symptoms, particularly those related to the heart and upper limbs. A detailed family history is also essential, as this syndrome follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis. Identifying mutations in the TBX5 gene can provide definitive evidence of the condition. Imaging techniques like echocardiograms help assess any cardiac defects.
Additionally, orthopedic assessments are vital to evaluate limb abnormalities. A multidisciplinary approach involving cardiologists and geneticists ensures comprehensive care for affected individuals, allowing tailored management plans based on their unique needs.
Prenatal Diagnosis and Screening
Prenatal diagnosis for Holt-Oram Syndrome is crucial for early intervention and family planning. Expecting parents can undergo genetic testing, which typically involves analyzing the fetus’s DNA through amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These procedures help identify mutations in the TBX5 gene associated with the syndrome.
Ultrasound examinations during pregnancy may also reveal physical abnormalities indicative of Holt-Oram Syndrome. Key markers include heart defects and upper limb malformations that can be detected as early as 18-20 weeks gestation.
Genetic counseling plays a vital role in guiding families through these processes. Counselors provide information on risks, implications of findings, and potential options available based on test results.
Cardiac Imaging in Holt-Oram Syndrome
Cardiac imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing Holt-Oram Syndrome. It helps identify structural heart defects associated with the condition, including atrial septal defects or ventricular septal defects.
Echocardiography is typically the first-line imaging technique due to its accessibility and ability to evaluate cardiac anatomy and function in real-time. This non-invasive procedure provides valuable insights into blood flow dynamics.
In some cases, advanced imaging modalities like MRI may be employed for more detailed assessments of complex cardiac anomalies. These methods enhance understanding of the patient’s unique cardiovascular status, guiding treatment decisions effectively.
Management of Cardiac Defects
Management of cardiac defects in Holt-Oram Syndrome primarily involves a multidisciplinary approach. Pediatric cardiologists play a crucial role in assessing the severity of heart anomalies. Early detection allows for timely interventions.
Treatment options may include medications to manage symptoms or surgical interventions to correct structural abnormalities. Procedures like catheter-based interventions can also be beneficial, depending on the specific defect.
Regular follow-up is essential to monitor heart function and address any complications that arise as patients grow older. This ongoing care ensures optimal health outcomes and supports overall well-being throughout life.
Orthopedic Interventions for Upper Limb Abnormalities
Individuals with Holt-Oram Syndrome often experience upper limb abnormalities, which can range from mild to severe. Orthopedic interventions aim to improve functionality and enhance quality of life. These procedures can involve surgery or non-invasive therapies depending on the patient’s needs.
Surgical options may include reconstructive surgeries that focus on enhancing limb structure and function. Techniques like tendon transfer or bone lengthening can help patients regain mobility and strength in their arms.
Non-surgical approaches might involve physical therapy, splints, or occupational therapy. These methods help develop motor skills and adapt daily activities for better independence. A personalized treatment plan is essential for achieving optimal results tailored to each individual’s circumstances.
Multidisciplinary Care Approach
A multidisciplinary care approach is essential for individuals with Holt-Oram Syndrome. This condition affects both the heart and upper limbs, requiring expertise from various healthcare professionals.
Cardiologists play a vital role in managing cardiac defects associated with the syndrome. They work closely with pediatricians to monitor growth and development in affected children. Orthopedic specialists are crucial for addressing upper limb abnormalities, providing tailored interventions to enhance mobility.
Additionally, genetic counselors help families understand inheritance patterns. Occupational therapists can assist patients in adapting daily activities to their abilities. This collaborative effort ensures comprehensive care that addresses all aspects of living with Holt-Oram Syndrome effectively.
Prognosis and Life Expectancy
The prognosis for individuals with Holt-Oram Syndrome varies based on the severity of cardiac and orthopedic manifestations. Many affected individuals lead fulfilling lives, especially when proper medical management is in place.
Life expectancy can be significantly influenced by the presence of congenital heart defects. Advances in cardiac care have improved outcomes, allowing many to live into adulthood.
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring potential complications. With early intervention and a tailored treatment plan, those diagnosed can achieve an excellent quality of life despite their challenges.
Quality of Life Considerations
Individuals with Holt-Oram Syndrome often face unique challenges that can impact their quality of life. Physical limitations due to upper limb abnormalities may affect daily activities, requiring adaptive tools and resources for greater independence.
Psychosocial aspects also play a significant role. Emotional support from family, friends, and professionals is crucial in helping affected individuals navigate social interactions and self-esteem issues.
Access to healthcare services ensures regular monitoring of cardiac health, which is essential for managing long-term outcomes effectively. Engaging in multidisciplinary care fosters improved management strategies tailored to the individual’s needs, enhancing overall well-being and encouraging an active lifestyle despite the syndrome’s challenges.
Holt-Oram Syndrome in Adulthood
Holt-Oram Syndrome often presents unique challenges in adulthood. As individuals grow, the manifestations of this genetic disorder may evolve. Many adults experience cardiac issues that require ongoing monitoring and management.
Upper limb abnormalities can also impact daily activities and employment opportunities. Those affected might explore adaptive technologies to enhance their quality of life. Occupational therapy plays a vital role in helping individuals maximize their capabilities.
Additionally, emotional well-being is crucial for adults living with Holt-Oram Syndrome. Support groups can provide a sense of community, allowing individuals to share experiences and strategies for coping with challenges they face throughout life’s journey.
Reproductive Considerations for Affected Individuals
Individuals with Holt-Oram Syndrome may face unique reproductive challenges. The genetic nature of the condition means that affected parents could pass on the TBX5 gene mutation to their children. This possibility raises important questions for family planning and genetic counseling.
Before starting a family, individuals should consider undergoing genetic testing. This can provide valuable insights into potential risks for offspring and help in making informed decisions about reproduction.
Additionally, healthcare providers can guide patients through pregnancy management if they choose to conceive. Monitoring cardiac health during pregnancy is essential due to potential complications associated with both maternal and fetal well-being.
Ongoing Research and Clinical Trials
Ongoing research into Holt-Oram Syndrome focuses on understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying the condition. Scientists are investigating TBX5 gene mutations to design targeted therapies that may improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Clinical trials are exploring novel treatments aimed at managing cardiac defects and upper limb abnormalities. These studies offer hope by aiming to refine surgical techniques and develop innovative rehabilitation strategies tailored for patients with this syndrome.
Researchers also aim to establish standardized protocols for early diagnosis and intervention, which could significantly enhance quality of life. Collaboration among geneticists, cardiologists, and orthopedic specialists is essential in advancing knowledge about Holt-Oram Syndrome and improving patient care.
Differential Diagnosis: Similar Genetic Syndromes
Holt-Oram Syndrome is often confused with other genetic conditions due to overlapping features. For instance, Turner syndrome and Noonan syndrome can present similar cardiac and skeletal abnormalities.
Congenital heart defects are common in these syndromes, complicating the diagnostic process. Other conditions like Poland syndrome may also share upper limb anomalies but lack significant cardiac involvement.
Accurate diagnosis relies on a careful review of clinical features, family history, and genetic testing. Healthcare providers must consider all potential similarities to ensure proper management strategies for affected individuals.
Understanding these differential diagnoses enhances care pathways for patients and aids in establishing effective treatment plans tailored to individual needs.


