De Barsy Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that can have profound effects on those who are affected. With its unique combination of symptoms, including skin abnormalities and developmental delays, understanding this condition is crucial for patients and families alike. As research progresses, more insights into the causes, diagnosis, and management of De Barsy Syndrome are emerging.
This article aims to shed light on everything you need to know about this complex syndrome—from its origins to the latest treatment approaches—empowering readers with knowledge and resources for living with or supporting someone affected by this condition. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a caregiver, or simply curious about genetic disorders, there’s something valuable here for everyone. Let’s dive deeper into De Barsy Syndrome!

What is De Barsy Syndrome?
De Barsy Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by distinct physical and developmental features. It primarily affects the skin, joints, and overall growth of an individual.
This condition is classified as a type of cutis laxa syndrome, which refers to the loose or sagging skin often seen in affected individuals. The symptoms can vary widely in severity from person to person.
“What Causes Eale’s Disease Syndrome? Vision Loss Guide”
First identified in 1971 by Dr. De Barsy, this syndrome has since gained recognition for its unique clinical presentation. Researchers continue to study it for better understanding and management options.
Individuals with De Barsy Syndrome may experience various challenges throughout their lives due to its complex nature. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for improving quality of life and supporting healthy development.
De Barsy Syndrome Definition and Overview
De Barsy Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects connective tissues in the body. It falls under the umbrella of cutis laxa syndromes, characterized by skin laxity and unique skeletal features.
Individuals with this syndrome may experience various symptoms, including distinctive facial features and developmental delays. The severity of these symptoms can vary widely among affected individuals.
“How Does Edwards Syndrome Affect Fetal Development?”
This condition results from specific mutations within genes responsible for collagen synthesis and cellular function. As such, those diagnosed often face a complex array of health challenges throughout their lives.
Understanding De Barsy Syndrome requires awareness not only of its physical manifestations but also its impact on overall quality of life. Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in managing the condition effectively and improving patient outcomes.
Historical Background and Discovery
De Barsy Syndrome was first described in 1981 by Dr. Henri De Barsy, a Belgian physician. His observations detailed a rare genetic disorder characterized by distinctive skin and skeletal abnormalities.
The syndrome gained attention as more cases emerged, leading to further research into its genetic underpinnings. Over the years, researchers identified an association between De Barsy Syndrome and mutations in the PYCR1 gene.
“What Causes Eisenmenger Syndrome? Heart Defect Guide”
This discovery marked a significant milestone in understanding the condition’s etiology. As knowledge of the syndrome expanded, it became clear that it posed unique challenges for affected individuals and their families.
In recent years, advancements in genetics have paved the way for improved diagnostic techniques and potential therapeutic strategies. Ongoing studies continue to explore this complex condition and its implications for those diagnosed with De Barsy Syndrome.
Causes of De Barsy Syndrome
De Barsy Syndrome primarily arises from genetic factors. It is classified as a rare connective tissue disorder, and its roots lie in specific mutations within the genes responsible for collagen synthesis.
One significant culprit is the PYCR1 gene. Mutations here disrupt normal cellular function, leading to a range of symptoms associated with De Barsy Syndrome.
The inheritance patterns are typically autosomal recessive. This means that both parents must carry and pass on the mutated gene for their child to be affected by this syndrome.
“Why Does Facet Syndrome Cause Back Pain? Complete Guide”
Understanding these genetic underpinnings can assist families in navigating potential risks and implications for future offspring. Genetic counseling often plays a crucial role in providing clarity around these inherited conditions. Effective management begins with grasping the causes at play, guiding families towards appropriate care strategies.
Genetic Factors
De Barsy Syndrome is primarily influenced by genetic factors. It is a rare disorder that arises from specific mutations within the genes responsible for collagen and elastic tissue formation.
The condition has been linked to alterations in the PYCR1 gene, which plays a crucial role in the metabolism of proline—a vital amino acid. Changes in this gene disrupt normal cellular functions, leading to various symptoms associated with De Barsy Syndrome.
“What Is Fazio-Londe Syndrome? Understanding Motor Neuron Disease”
These genetic mutations can be inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means that both parents must carry a copy of the mutated gene for their child to be affected by the syndrome. Understanding these genetic factors helps healthcare providers offer better diagnostic and therapeutic options for individuals impacted by this condition.
PYCR1 Gene Mutations
PYCR1 gene mutations play a crucial role in the development of De Barsy Syndrome. This gene is responsible for encoding an enzyme involved in proline synthesis, which is vital for maintaining healthy connective tissues.
When mutations occur within the PYCR1 gene, it can disrupt normal collagen production. This disruption leads to various skin abnormalities and other symptoms associated with De Barsy Syndrome.
“How Does Femoral Acetabular Impingement Affect Hip Movement?”
Research indicates that these mutations often result in a reduction or complete loss of enzyme function. Consequently, this affects not only physical appearance but also overall health and development.
Understanding how PYCR1 mutations contribute to clinical manifestations helps researchers identify potential therapeutic targets. Continued investigation into these genetic changes may pave the way for improved management strategies tailored to individual needs.
Inheritance Patterns
Inheritance patterns in De Barsy Syndrome primarily follow an autosomal recessive model. This means that two copies of the mutated gene, one inherited from each parent, are necessary for a child to be affected by the disorder.
Parents who carry one copy of the mutation typically do not show symptoms. However, they have a 25% chance of passing on both copies of the mutated gene to their offspring if both parents are carriers.
“What Triggers Fibromyalgia Syndrome? Pain Management Guide”
This pattern highlights the importance of genetic counseling for families with a history of De Barsy Syndrome. Understanding these inheritance dynamics can help potential parents make informed decisions about family planning and assess risks associated with future pregnancies.
Awareness and knowledge can empower individuals and families navigating this complex genetic landscape.
De Barsy Syndrome Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
De Barsy Syndrome presents a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Skin abnormalities often include loose, sagging skin that may resemble conditions like cutis laxa. This distinctive feature is one of the first signs observed in affected individuals.
Facial features are also characteristic. Affected individuals may have prominent foreheads, deep-set eyes, and other unique craniofacial traits. These characteristics contribute to a recognizable appearance among those with the syndrome.
Skeletal and joint issues are common as well, leading to flexibility problems or misalignment in bones and joints. Developmental delays frequently accompany these physical manifestations, affecting motor skills and cognitive development.
Neurological symptoms can arise too—ranging from mild developmental challenges to more significant neurological disorders. Each symptom plays a crucial role in understanding this complex condition and its diverse impacts on daily living.
Skin Abnormalities
Individuals with De Barsy Syndrome often experience distinctive skin abnormalities. These can include loose, elastic skin that may appear thin and fragile. The condition is marked by a notable lack of elasticity, which can lead to increased vulnerability to injuries.
Some patients may also develop various lesions or discolorations on their skin. These changes are not just cosmetic; they can affect the overall health of the individual. Skin integrity is crucial for protection against infections and environmental factors.
Additionally, individuals might present with unusual scarring patterns. The healing process in those affected by De Barsy Syndrome tends to be slower than average, resulting in more prominent scars over time.
Managing these skin issues requires careful attention from healthcare providers specialized in dermatology as part of a comprehensive treatment plan tailored for each patient’s needs.
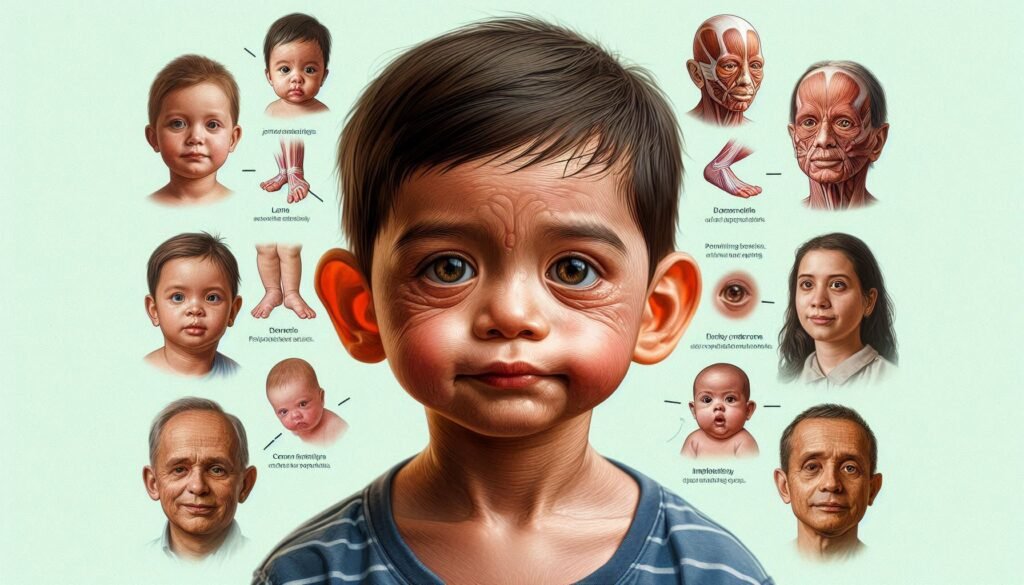
Facial Features
Individuals with De Barsy Syndrome often exhibit distinctive facial features. These characteristics are primarily due to the underlying connective tissue abnormalities caused by genetic mutations.
One notable feature is a prominent forehead, which can give the face an elongated appearance. The eyebrows may appear thick and sometimes merge in the center, creating a unibrow effect.
Additionally, individuals might have deep-set eyes that contribute to their unique look. The nose can be broad or flattened at the bridge, further distinguishing these patients’ profiles.
Mouth anomalies are also common; many have thin lips or an underdeveloped jawline. This combination of traits results in a recognizable facial structure that helps in identifying those affected by this syndrome.
Understanding these features is crucial for medical professionals when diagnosing and managing De Barsy Syndrome effectively.
Skeletal and Joint Issues
Skeletal and joint issues are prominent features of De Barsy Syndrome. Individuals often exhibit a range of abnormalities affecting bone structure and function.
Joint hypermobility is common, leading to instability. This can cause discomfort and increase the risk of injuries. Some may also experience early-onset arthritis due to the wear and tear on affected joints.
Short stature is another key characteristic associated with this syndrome. Growth patterns can deviate from typical developmental milestones, resulting in noticeable height differences compared to peers.
Additionally, scoliosis or spinal deformities may arise over time. These conditions require careful monitoring as they can impact mobility and overall quality of life. Regular orthopedic assessments play a crucial role in managing these skeletal challenges effectively.
Developmental Delays due to De Barsy Syndrome
Developmental delays are a significant aspect of De Barsy Syndrome that can affect various areas of growth and learning. Children with this condition often experience challenges in reaching developmental milestones, such as walking or speaking.
These delays stem from the underlying genetic factors affecting brain development and function. As a result, cognitive abilities may be impacted, leading to difficulties in communication and social interaction.
In addition to motor skills, affected individuals might struggle with adaptive behaviors. Everyday tasks like self-care can pose challenges due to coordination issues or limited fine motor skills.
Early intervention is crucial for addressing these developmental concerns. Tailored therapies focusing on speech, occupational skills, and physical movement can provide essential support for children navigating these hurdles. A multidisciplinary approach ensures that each child receives comprehensive care tailored to their unique needs.
Neurological Manifestations
Neurological manifestations in De Barsy Syndrome are significant and can vary widely among individuals. These symptoms often stem from the underlying genetic mutations that affect brain development and function.
Common neurological issues include developmental delays, which may impact motor skills, speech, and cognitive abilities. Children with this syndrome might show slower progress in reaching developmental milestones compared to their peers.
Seizures can also occur, adding another layer of complexity to the condition. The frequency and severity of seizures differ among patients.
Additionally, some individuals may experience behavioral challenges or changes in mood regulation. Early intervention through therapies is essential for addressing these neurological concerns effectively. Understanding the full spectrum of neurological symptoms helps families manage care more efficiently while providing support tailored to each individual’s needs.
Diagnosis of De Barsy Syndrome
Diagnosing De Barsy Syndrome involves a comprehensive clinical evaluation. Physicians assess the patient’s medical history and conduct a physical examination. Specific attention is given to skin, skeletal features, and overall development.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis. It identifies mutations in specific genes associated with the syndrome, particularly those affecting connective tissue.
Differential diagnosis is essential to distinguish De Barsy Syndrome from similar conditions. Clinicians consider other genetic disorders that present with overlapping symptoms, such as Cutis Laxa Syndromes or Progeroid Syndromes. This careful analysis ensures accurate identification and appropriate management of the condition.
Clinical Evaluation
Clinical evaluation is a critical first step in diagnosing De Barsy Syndrome. It typically involves a thorough physical examination led by a healthcare professional who specializes in genetic disorders. During this assessment, the clinician looks for distinctive symptoms associated with the syndrome.
Healthcare providers often pay close attention to skin abnormalities, facial features, and joint issues that manifest in affected individuals. A detailed medical history of the patient and family can provide additional context that aids diagnosis.
The clinical evaluation may also involve observing developmental milestones to identify delays or other neurological concerns. These observations form an essential part of understanding how De Barsy Syndrome impacts each individual differently, guiding further diagnostic steps such as genetic testing when necessary.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing De Barsy Syndrome. This process involves analyzing an individual’s DNA to identify specific mutations linked to the condition.
For those suspected of having this syndrome, a blood sample is often taken. The sample undergoes detailed analysis, focusing on genes associated with skin, skeletal, and neurological features of the disorder.
Identifying PYCR1 gene mutations can confirm a diagnosis. These genetic insights help healthcare professionals understand the severity and implications of the syndrome for each patient.
Moreover, genetic testing provides valuable information for family planning. It allows parents to assess their risk of passing on hereditary conditions.
These tests empower families with knowledge about potential health challenges and management strategies tailored to individual needs.
Differential Diagnosis of De Barsy Syndrome
Differential diagnosis is crucial when assessing De Barsy Syndrome. Several conditions present similar symptoms and features, making accurate identification essential.
Cutis laxa syndromes often overlap in clinical presentation. These conditions also involve skin laxity and skeletal abnormalities, which can confuse the diagnostic process.
Progeroid syndromes are another group to consider. They may exhibit premature aging signs alongside developmental delays, resembling aspects of De Barsy Syndrome.
Other connective tissue disorders might share characteristics as well. Conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome can create challenges in distinguishing them from De Barsy Syndrome due to overlapping symptoms such as joint hypermobility.
A thorough patient history and comprehensive evaluations play pivotal roles in refining the diagnosis. Genetic testing further aids healthcare professionals in differentiating between these complex syndromes effectively.
Treatment and Management of De Barsy Syndrome
Managing De Barsy Syndrome requires a multidisciplinary approach. This ensures that all aspects of the condition are addressed effectively. Team members may include dermatologists, orthopedic specialists, neurologists, and therapists.
Dermatological care focuses on treating skin abnormalities to enhance comfort and appearance. Regular assessments help in managing these issues proactively.
Orthopedic interventions are vital for addressing skeletal and joint problems. Physical therapy can improve mobility and reduce pain associated with these challenges.
Developmental therapy is crucial for children with De Barsy Syndrome. Tailored programs support learning milestones and social skills development.
Neurological management involves regular monitoring for cognitive or behavioral changes. Early intervention can optimize outcomes in this area as well.
This comprehensive strategy not only addresses physical symptoms but also promotes overall well-being for individuals living with this syndrome.
Multidisciplinary Approach
A multidisciplinary approach is essential for effectively managing De Barsy Syndrome. This condition affects multiple systems in the body, requiring input from various healthcare professionals.
Collaboration among specialists ensures comprehensive care. Dermatologists address skin abnormalities while orthopedic surgeons focus on skeletal and joint issues. Pediatricians play a crucial role in monitoring overall development.
Speech therapists and occupational therapists contribute to developmental support. Their expertise helps improve communication skills and daily living activities for affected individuals.
Regular consultations among team members foster an integrated treatment plan tailored to each patient’s unique needs. Such teamwork enhances the quality of life for those living with De Barsy Syndrome, providing holistic support that encompasses physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of health.
This dynamic approach not only improves outcomes but also encourages families to feel supported throughout their journey with this rare syndrome.
Dermatological Care
Dermatological care is crucial for individuals with De Barsy Syndrome. Skin abnormalities can manifest as loose, sagging skin and other irregularities. These conditions may lead to discomfort or an increased risk of infections.
Regular consultations with a dermatologist help monitor these changes. Customized skincare routines play a vital role in maintaining skin health. Moisturizers and gentle cleansers are often recommended to soothe sensitive areas.
In some cases, specialized treatments like laser therapy might be beneficial. This can improve the appearance of skin lesions or scarring associated with the syndrome.
Education about sun protection is also essential. Patients should use broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect their fragile skin from UV damage, reducing the risk of further complications.
Proactive dermatological management significantly enhances quality of life for those affected by De Barsy Syndrome.
Orthopedic Interventions
Orthopedic interventions play a crucial role in managing the musculoskeletal issues associated with De Barsy Syndrome. Individuals often experience joint problems and skeletal abnormalities that require specialized care.
Treatment may involve physical therapy to enhance movement and strengthen muscles. This approach can help improve overall mobility, making daily activities easier for patients.
In some cases, surgical options are explored to correct significant deformities or stabilize joints. These procedures aim to alleviate pain and enhance functionality.
Custom orthotics may also be recommended. They provide support and alignment for the feet, which is essential for those with abnormal gait patterns caused by their condition.
Regular follow-ups with orthopedic specialists ensure that treatment plans adapt as needed over time. This proactive management is vital in addressing ongoing challenges related to skeletal health in De Barsy Syndrome patients.
Developmental Therapy
Developmental therapy plays a crucial role in managing De Barsy Syndrome. This specialized approach focuses on enhancing the child’s overall development across various domains.
Therapists employ tailored strategies to improve motor skills, speech, and cognitive abilities. Activities are designed to engage children at their individual levels of understanding and capability.
Play-based interventions often make sessions enjoyable for young patients. These methods encourage social interaction while addressing specific developmental delays characteristic of the syndrome.
Parental involvement is vital in this process. Training parents to implement therapeutic techniques at home fosters continuity and reinforces learned skills.
Regular assessments help track progress and adjust goals as necessary. By fostering an environment where children can thrive, developmental therapy significantly enhances quality of life for those affected by De Barsy Syndrome.
Neurological Management
Neurological management for individuals with De Barsy Syndrome is essential due to the potential for cognitive and motor challenges. A specialized healthcare team typically evaluates neurological function regularly. This ensures that any emerging issues are identified early.
Therapies may include physical, occupational, and speech therapy tailored to improve communication skills and enhance daily functioning. These therapies help foster independence and boost confidence in affected individuals.
Medical professionals might also prescribe medications to address seizures or other neurological symptoms as needed. Regular follow-ups with neurologists can aid in adjusting treatment plans based on individual progress.
Incorporating routine assessments helps track developmental milestones. It also provides necessary adjustments to interventions, facilitating a more supportive environment for overall well-being. Creating an engaging atmosphere at home is crucial as it encourages participation in activities that stimulate cognitive growth.
Living with De Barsy Syndrome
Living with De Barsy Syndrome presents daily challenges for individuals and their families. The variety and severity of symptoms can impact everyday activities significantly. Simple tasks may require extra time, patience, and support.
Social interactions can also be difficult due to visible skin abnormalities or developmental delays. These factors sometimes lead to feelings of isolation for those affected. Understanding from peers is crucial in fostering inclusive environments.
Support systems play a vital role in managing life with this condition. Engaging with healthcare professionals who specialize in multidisciplinary care helps address the diverse needs associated with De Barsy Syndrome.
Family support is equally important, offering emotional stability and encouragement through various hurdles. Connecting with local or online communities allows individuals to share experiences and resources, creating a network that promotes resilience and hope amid challenges.
Daily Challenges
Living with De Barsy Syndrome often presents a range of daily challenges for affected individuals and their families. Skin abnormalities can lead to discomfort and increased sensitivity, making routine activities like bathing or dressing difficult.
Mobility issues may arise due to skeletal and joint problems. This can restrict participation in play or exercise, impacting overall well-being. Daily tasks may require additional support or adaptive equipment.
Developmental delays add another layer of complexity. Children might need tailored educational strategies to thrive academically and socially. Navigating these needs requires patience and understanding from caregivers.
Social interactions can be hindered by the visible aspects of the syndrome, leading to feelings of isolation. Building a supportive community becomes essential for both emotional resilience and practical help in managing everyday life.
Support Systems
Support systems play a crucial role for individuals impacted by De Barsy Syndrome. These networks can include family, friends, healthcare providers, and community organizations.
Family members often provide emotional stability and practical assistance. They help manage daily routines and advocate for appropriate care.
Healthcare professionals contribute specialized knowledge essential for managing symptoms effectively. This includes pediatricians, geneticists, dermatologists, and neurologists who collaborate to create comprehensive care plans.
Community support groups offer invaluable resources as well. Connecting with others facing similar challenges fosters understanding and shared experiences.
Online forums also serve as platforms where families can exchange information about treatments or coping strategies. Accessing these diverse support options empowers patients and caregivers alike in navigating the complexities of De Barsy Syndrome.
Research and Future Prospects
Research on De Barsy Syndrome is progressively advancing, with scientists exploring various aspects of this rare condition. Current studies focus on the genetic underpinnings and how mutations in the PYCR1 gene contribute to its development.
Potential therapies are being investigated, including targeted treatments that address specific symptoms. Researchers aim to develop more effective management strategies tailored to individual patient needs.
Genetic counseling remains a crucial component for families affected by De Barsy Syndrome. It provides essential insight into inheritance patterns and helps parents understand their risks for future pregnancies.
Continued collaboration among medical professionals, researchers, and families can enhance understanding of this syndrome. As awareness grows, so does the hope for breakthrough discoveries that could significantly improve patients’ quality of life.
Current Studies
Current studies on De Barsy Syndrome are delving into the underlying genetic mechanisms that contribute to this rare condition. Researchers focus on identifying novel mutations in the PYCR1 gene and how they affect collagen synthesis.
Ongoing clinical trials aim to better understand the range of symptoms associated with De Barsy Syndrome. These investigations help in establishing more precise diagnostic criteria, which may lead to earlier detection.
Additionally, collaboration among medical professionals is fostering a multidisciplinary approach. This research makes strides toward understanding treatment options tailored specifically for affected individuals.
There is also an emphasis on patient registries aimed at gathering comprehensive data from families impacted by this syndrome. Such efforts enhance awareness and support future therapeutic developments.
Potential Therapies
Research into potential therapies for De Barsy Syndrome is an evolving field. Scientists are exploring various approaches that could improve the quality of life for those affected.
Gene therapy holds promise as a way to address the underlying genetic mutations associated with the syndrome. By targeting specific genes, researchers hope to correct or mitigate the effects of PYCR1 gene mutations.
Pharmacological interventions are also being studied. These may include drugs aimed at managing symptoms such as skin abnormalities and joint issues.
Additionally, ongoing clinical trials are assessing new treatment protocols that focus on interdisciplinary care involving dermatologists, orthopedic specialists, and neurologists.
Supportive therapies like physical and occupational therapy can enhance mobility and independence. Researchers emphasize the importance of personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s needs and challenges in living with De Barsy Syndrome.
Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling plays a crucial role for families affected by De Barsy Syndrome. It provides individuals with essential information about the genetic aspects of this rare condition.
During sessions, counselors explain how the PYCR1 gene mutations impact inheritance. They clarify risks for future pregnancies and offer insights into the likelihood of other family members carrying similar genetic variants.
Counselors also help families navigate emotional challenges related to diagnosis and management. It’s a supportive space where questions can be asked without judgment.
Additionally, they may provide resources for support groups or educational materials to help families understand daily living with De Barsy Syndrome better. This guidance empowers parents and caregivers as they make informed choices regarding medical care and therapies available for their loved ones.
De Barsy Syndrome vs. Similar Conditions
De Barsy Syndrome shares characteristics with several other genetic conditions, particularly cutis laxa syndromes. These disorders also involve skin laxity and connective tissue abnormalities but may differ in their underlying genetic causes and clinical presentations.
Progeroid syndromes are another group that can be confused with De Barsy Syndrome. While both result in premature aging signs, progeroid syndromes typically have distinct features like severe growth retardation and unique facial changes not seen in De Barsy patients.
Differentiating these conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management. Genetic testing plays a key role here, as it helps identify specific mutations linked to each syndrome. Understanding the nuances between these similar conditions aids healthcare providers in offering appropriate care tailored to individual patient needs.
Cutis Laxa Syndromes
Cutis Laxa syndromes represent a group of rare genetic disorders characterized by loose, sagging skin. This condition results from the abnormal production or structure of elastic fibers in connective tissue.
Individuals with Cutis Laxa often experience not only skin laxity but also other systemic issues. These can include joint hypermobility and various internal organ complications due to weakened connective tissues.
The syndromes vary significantly in severity and associated features. Some forms are inherited through autosomal dominant patterns, while others follow an autosomal recessive inheritance model.
Diagnosis typically involves clinical evaluation along with genetic testing to identify specific mutations linked to the condition. Treatment is largely supportive, focusing on managing symptoms and improving quality of life for those affected by these challenging syndromes.
Progeroid Syndromes
Progeroid syndromes represent a diverse group of genetic disorders that mimic the physical signs of aging at an accelerated rate. While De Barsy Syndrome primarily affects connective tissue, leading to various skin and skeletal abnormalities, progeroid syndromes like Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria are characterized by distinct facial features and rapid biological aging.
Unlike De Barsy Syndrome, which often involves joint issues and developmental delays, progeroid conditions typically exhibit symptoms such as growth failure and cardiovascular complications early in life. Although both groups share some overlapping characteristics—like changes in skin elasticity—the underlying genetic causes differ significantly.
Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management strategies. Ongoing research aims to unravel the complexities of these conditions further while providing hope for targeted therapies. As scientists delve deeper into genetics, they pave the way toward better treatment options not just for individuals with De Barsy Syndrome but also for those affected by similar disorders, ultimately improving quality of life across the spectrum of connective tissue diseases.