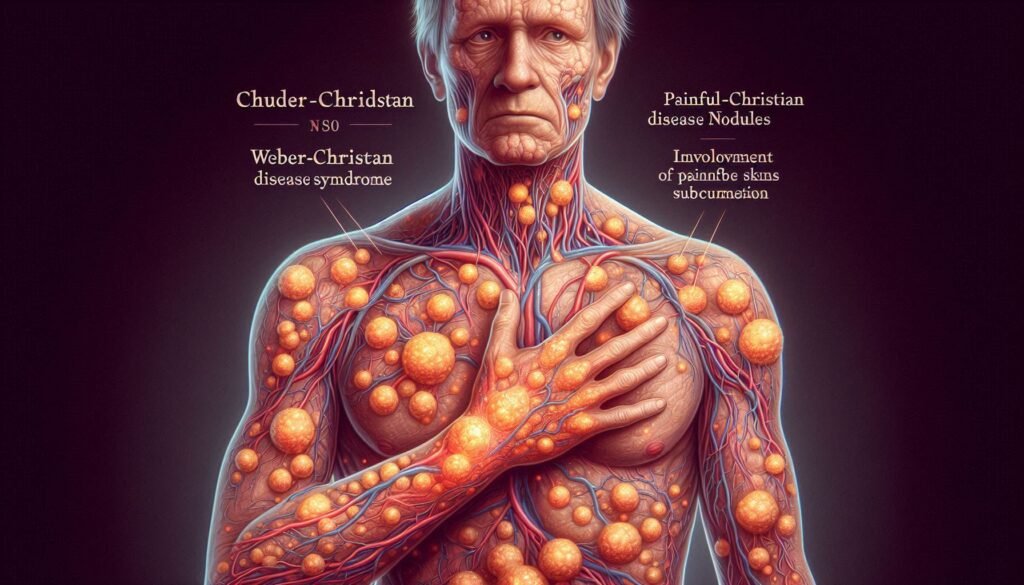
Defining Weber-Christian Disease: An Introduction to the Rare Condition
Weber-Christian Disease, though rare, is a fascinating condition that warrants attention. This inflammatory disorder can impact various body systems and often leaves those affected seeking answers. Understanding Weber-Christian Disease is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike.
This disease presents unique challenges due to its elusive nature and varied symptoms. From skin nodules to systemic manifestations, the journey through diagnosis and treatment can be complex. As awareness grows, it’s crucial to explore what defines this condition, how it develops, and what options exist for managing its effects on daily life.
Join us as we delve into the details of Weber-Christian Disease—its causes, symptoms, treatment approaches—and shed light on an often-overlooked topic in the realm of autoimmune disorders. Whether you’re a patient navigating your health or simply curious about this intriguing condition, there’s much to discover here.
Historical Perspective: Discovery and Naming of Weber-Christian Disease
Weber-Christian Disease, a rare inflammatory condition, has a fascinating history rooted in its discovery. The disease was first identified in the early 20th century. Two prominent figures played pivotal roles: Dr. Karl Weber and Dr. Christian.
Dr. Weber, an Austrian physician, described cases of patients presenting with painful nodules and systemic symptoms that defied traditional classification. Around the same time, Dr. Christian contributed significant observations regarding the skin lesions associated with these cases.
“Why Does Bloom Syndrome Increase Cancer Risk? Complete Guide”
Their combined efforts led to the formal nomenclature of Weber-Christian Disease in recognition of their contributions to understanding this complex condition. As research progressed over decades, it became clear that this illness encompasses not just dermatological manifestations but also systemic involvement.
The historical context highlights how collaborative clinical observation can lead to better awareness and knowledge about rare diseases like Weber-Christian Disease.
Pathophysiology of Weber-Christian Disease: Understanding the Inflammation Process
Weber-Christian Disease is characterized by an abnormal inflammatory response. This condition primarily involves the infiltration of immune cells into various tissues.
The inflammation typically affects adipose tissue, leading to painful nodules and a range of systemic symptoms. In this disease, the immune system mistakenly targets its own fat cells, causing localized swelling and discomfort.
“What Is Boerhaave Syndrome & Why Is It A Medical Emergency?”
Cytokines play a crucial role in driving this process. These signaling molecules promote inflammation and can lead to further complications if not managed properly.
Moreover, the vascular component cannot be overlooked. Blood vessels may become involved, contributing to skin changes and pain associated with Weber-Christian Disease.
Understanding these mechanisms provides insight into potential treatment strategies aimed at reducing inflammation and restoring normal function within affected tissues. The goal remains focused on mitigating symptoms while improving patient quality of life through targeted interventions.
Clinical Manifestations: Characteristic Symptoms of Weber-Christian Disease
Weber-Christian Disease presents a range of clinical symptoms that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. One of the hallmark features is painful subcutaneous nodules, which often appear on the limbs and trunk. These nodules may vary in size and tenderness.
“How Does Budd-Chiari Syndrome Affect Your Liver? Expert Explained”
Fever, malaise, and fatigue are common systemic symptoms associated with this condition. Patients frequently report an overall sense of unwellness that can complicate daily activities.
Additionally, some individuals experience joint pain or arthralgia. This discomfort can mimic other rheumatologic conditions, making diagnosis challenging.
Weight loss is another concerning symptom; it reflects the body’s response to chronic inflammation.
Skin changes such as erythema or purpura may also be evident, adding to the array of manifestations that characterize Weber-Christian Disease. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and management strategies.
Cutaneous Manifestations: Nodules and Skin Changes
Cutaneous manifestations are a hallmark of Weber-Christian Disease, often leading to initial diagnosis. Patients typically present with tender nodules that can appear on various parts of the body. These painful subcutaneous lumps may vary in size and location.
“What Causes Buschke-Ollendorff Syndrome? Skin & Bone Guide”
The skin changes associated with this condition are not just cosmetic; they signify underlying inflammation. These nodules can become erythematous and warm to touch, indicating active inflammation beneath the surface.
In some cases, patients may experience ulceration or scarring as the disease progresses. This adds another layer of complexity to management and treatment.
Identifying these skin changes early is crucial for timely intervention and effective therapy. Dermatologists play an essential role in recognizing these signs during examinations, providing invaluable insights into diagnosing Weber-Christian Disease accurately.
Systemic Involvement in Weber-Christian Disease
Weber-Christian Disease is not just a localized condition; it can impact multiple organ systems. Systemic involvement often manifests as fever, malaise, and weight loss. Patients may experience fatigue that affects daily life.
“Why Is It Called Baboon Syndrome? Understanding SDRIFE”
The disease can also lead to complications in the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms like abdominal pain or diarrhea might arise due to inflammation of the intestinal lining.
Musculoskeletal issues are common as well. Many individuals report joint pain and stiffness, which can significantly hinder mobility.
Additionally, respiratory symptoms may occur when lung tissue becomes involved. This could present as cough or shortness of breath, requiring further evaluation.
Recognizing systemic manifestations is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment strategies. Addressing these broader implications improves patient outcomes and quality of life significantly.
Diagnostic Criteria and Challenges in Weber-Christian Disease
Diagnosis of Weber-Christian Disease poses unique challenges due to its rarity and overlapping symptoms with other conditions. Clinicians often rely on a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
“What Is Banti’s Syndrome & How Does It Affect The Spleen?”
The diagnostic criteria typically include the presence of painful subcutaneous nodules or plaques, elevated inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), and exclusion of other similar diseases.
However, there is no single definitive test for this condition. The subtlety in manifestations can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
Moreover, histopathological examination plays a crucial role in confirming inflammation patterns characteristic of Weber-Christian Disease but may not always be readily available.
Physicians must remain vigilant and consider patient history extensively to ensure accurate diagnosis while navigating these complexities. Each patient’s presentation may differ significantly, adding another layer of difficulty in achieving clarity within the diagnosis process.
Laboratory Findings and Biomarkers in Weber-Christian Disease
Laboratory findings play a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of Weber-Christian Disease. Blood tests often reveal elevated inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). These indicators suggest an active inflammatory process.
“How Does Barlow’s Syndrome Impact Heart Valve Function?”
Additionally, specific biomarkers can aid clinicians in understanding disease activity. For instance, serum amyloid A levels may also be increased during flare-ups of the condition.
While no single test confirms Weber-Christian Disease, autoimmune panel tests are conducted to rule out similar disorders. This helps narrow down potential diagnoses effectively.
Furthermore, imaging studies complement laboratory results by visualizing nodules or other affected areas. The combination of lab findings and clinical symptoms provides a comprehensive view that guides treatment decisions for patients dealing with this rare condition.
Imaging Studies: Role in Diagnosis and Monitoring
Imaging studies play a vital role in the diagnosis and monitoring of Weber-Christian Disease. These non-invasive techniques help visualize inflammation and assess the extent of tissue involvement.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is particularly valuable for evaluating soft tissues. It can highlight areas affected by nodular lesions, providing insights into disease activity. MRI findings often correlate with clinical symptoms, guiding treatment decisions.
Ultrasound is another useful tool, allowing clinicians to detect subcutaneous nodules or masses early on. This method helps monitor changes over time without exposing patients to radiation.
Computed tomography (CT) scans may also assist in identifying any systemic involvement, especially when assessing internal organs. They provide detailed cross-sectional images that can reveal hidden complications associated with this rare condition.
Imaging studies are integral to understanding Weber-Christian Disease’s progression and tailoring appropriate management strategies for affected individuals.
Histopathological Features of Weber-Christian Disease
Histopathological examination plays a crucial role in diagnosing Weber-Christian Disease. The hallmark feature is the presence of lobular panniculitis, which involves inflammation of the fat layer beneath the skin.
Under microscopic evaluation, one can observe a dense infiltrate of neutrophils and lymphocytes. This inflammatory cell aggregation contributes to tissue damage and nodules characteristic of the disease.
Additionally, necrosis may occur within adipose tissue, leading to significant clinical symptoms. Such findings help differentiate Weber-Christian from other conditions that also present with similar skin manifestations.
Special stains may reveal areas of fibrosis or granuloma formation in some cases. These histopathological features not only assist in diagnosis but also provide insights into the underlying inflammatory processes at play in this rare condition.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing Weber-Christian from Similar Conditions
Differential diagnosis is crucial in identifying Weber-Christian Disease. This rare condition shares symptoms with several other disorders, making accurate assessment challenging.
Conditions such as sarcoidosis and granulomatosis can present similar nodules or systemic inflammation. Therefore, distinguishing between these diseases often requires a thorough clinical evaluation.
Another key consideration is the potential overlap with autoimmune conditions like lupus erythematosus or dermatomyositis. These diseases may also exhibit skin manifestations that resemble those of Weber-Christian Disease.
Laboratory tests and imaging studies play vital roles in this differentiation process. Elevated inflammatory markers might suggest various underlying issues, necessitating a comprehensive approach to diagnostics.
Histopathological examination remains one of the most definitive methods for confirming Weber-Christian Disease versus its mimickers. Understanding these distinctions helps guide appropriate treatment strategies for each patient’s unique situation.
Treatment Approaches: Managing Inflammation and Symptoms
Managing Weber-Christian Disease involves a multifaceted approach aimed at reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual, as responses can vary widely among patients.
Corticosteroids remain a cornerstone in managing this condition. These medications help control inflammation and provide rapid relief from symptoms. However, long-term use may pose additional risks.
In addition to corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine or methotrexate may be utilized. These drugs work by dampening the immune response, potentially offering more sustained control over disease activity.
Biological therapies have emerged as promising options for harder-to-treat cases of Weber-Christian Disease. Agents targeting specific pathways in the immune system can lead to significant improvements for some patients.
Supportive care is equally important. This includes pain management strategies and physiotherapy to enhance mobility and quality of life while addressing any psychosocial aspects related to living with this rare condition.
Corticosteroid Therapy in Weber-Christian Disease
Corticosteroid therapy is a cornerstone in the management of Weber-Christian Disease. These anti-inflammatory medications help reduce the immune response, targeting the underlying inflammation that characterizes this condition.
Typically, corticosteroids are administered orally or via injection. The choice depends on the severity of symptoms and individual patient needs. Rapid symptom relief can often be seen with appropriate dosages.
Despite their effectiveness, long-term use may lead to potential side effects such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased susceptibility to infections. Therefore, doctors carefully monitor patients throughout treatment.
Tapering off corticosteroids gradually is crucial to avoid withdrawal symptoms and flares of disease activity. Each patient’s response varies significantly; thus, personalized treatment plans are essential for optimal outcomes in managing Weber-Christian Disease.
Immunosuppressive Agents and Their Role in Treatment
Immunosuppressive agents play a crucial role in the management of Weber-Christian Disease. These medications target the overactive immune response that characterizes this condition.
Commonly prescribed immunosuppressants include methotrexate and azathioprine. They help reduce inflammation by dampening immune system activity, leading to symptom relief.
Monitoring is essential while on these drugs. Regular blood tests are required to assess liver function and blood cell counts. This ensures patient safety during treatment.
Patients often experience varying responses to these agents. Some may achieve significant improvement, while others might require adjustments or alternative therapies.
The choice of an immunosuppressant depends on individual health factors and disease severity. Collaboration between healthcare providers and patients is vital for optimizing treatment outcomes with minimal side effects.
Biological Therapies: Emerging Options for Weber-Christian Disease
Biological therapies are gaining attention as innovative treatments for Weber-Christian Disease. These advanced medications target specific components of the immune system, offering new hope for patients.
Recent studies suggest that biologics can reduce inflammation and improve skin lesions associated with the condition. Drugs such as monoclonal antibodies may inhibit pathways involved in inflammatory responses, potentially leading to better management of symptoms.
One promising area of research focuses on agents targeting interleukins or tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Such targeted therapies aim to modify the disease’s course rather than simply alleviating symptoms.
Patients may experience fewer side effects compared to traditional immunosuppressive drugs. As more clinical trials emerge, the effectiveness and safety profile of these therapies will become clearer.
As researchers continue exploring biological options, they pave the way for personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. This approach could revolutionize how Weber-Christian Disease is managed in clinical practice.
Supportive Care and Symptom Management
Supportive care plays a vital role in managing Weber-Christian Disease. It focuses on alleviating symptoms and enhancing the patient’s quality of life.
Multidisciplinary approaches often prove beneficial. Physical therapists can help improve mobility, while occupational therapy assists with daily activities. Both contribute to maintaining independence.
Pain management is crucial, as discomfort may be persistent due to inflammation. Non-opioid analgesics can provide relief, but it’s essential for patients to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor pain management strategies.
Nutritional support also deserves attention. Patients may experience weight changes or gastrointestinal issues due to the disease or treatments. Consulting a registered dietitian can ensure adequate nutrient intake and overall health maintenance.
Psychosocial support cannot be overlooked either. Counseling services offer emotional assistance, helping individuals cope with anxiety or depression linked to chronic illness. Connecting with support groups fosters community and understanding among those facing similar challenges.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook for Patients
The prognosis for patients with Weber-Christian Disease varies widely. Factors influencing outcomes include the severity of the disease and individual response to treatment. While some may experience mild symptoms, others could have significant health challenges.
Long-term management is crucial. With appropriate therapy, many patients can achieve remission or at least manage their symptoms effectively. Regular monitoring helps in adjusting treatments as needed.
Complications can arise if the condition remains untreated or inadequately managed. This emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and intervention.
Patients often benefit from a multidisciplinary approach involving dermatologists, rheumatologists, and primary care providers. Emotional support also plays a vital role in improving quality of life for those affected by this rare condition.
Research into better treatment options continues to evolve, offering hope for improved prognostic outcomes in future cases of Weber-Christian Disease.
Quality of Life Considerations in Weber-Christian Disease
Living with Weber-Christian Disease can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. The unpredictable nature of symptoms often leads to physical discomfort and emotional distress.
Patients may experience chronic pain due to inflammation, which can limit daily activities. This limitation affects their ability to work, socialize, or even engage in simple pleasures.
Emotional health is equally crucial. Anxiety and depression are common among individuals coping with this rare condition. Support from healthcare providers and loved ones plays an essential role in managing these feelings.
Accessing accurate information about the disease empowers patients. Understanding treatment options fosters hope and encourages proactive health management strategies.
Creating a personalized care plan that includes both medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments can enhance overall wellbeing. Regular communication with healthcare professionals ensures that patients feel supported throughout their journey.
Current Research and Clinical Trials in Weber-Christian Disease
Current research and clinical trials are crucial for advancing our understanding of Weber-Christian Disease. Researchers are exploring various aspects, including the underlying mechanisms that trigger the inflammatory process associated with this condition. Ongoing studies aim to identify specific biomarkers that can aid in early diagnosis and effective monitoring.
Clinical trials focusing on new treatment modalities are also underway. These include evaluating the efficacy of novel biological therapies designed to target the immune system more precisely. Such advancements could lead to improved outcomes for patients suffering from Weber-Christian Disease by minimizing side effects and enhancing overall quality of life.
Moreover, collaborative efforts among healthcare professionals, researchers, and patient advocacy groups play a significant role in fostering awareness about this rare disease. This collective approach is essential not only for gathering data but also for providing support networks for those affected.
As research continues to progress, it holds promise for better diagnostic tools, innovative treatments, and ultimately a deeper understanding of Weber-Christian Disease. Keeping an eye on these developments will be vital for patients seeking effective management options as well as healthcare providers aiming to deliver optimal care.