Defining VATER Syndrome: An Introduction to the Condition
VATER Syndrome is a rare but complex condition that affects various parts of the body. It can be overwhelming for families navigating its many challenges, from diagnosis to management. Understanding this syndrome is crucial not only for those directly impacted but also for healthcare providers and educators involved in their care.
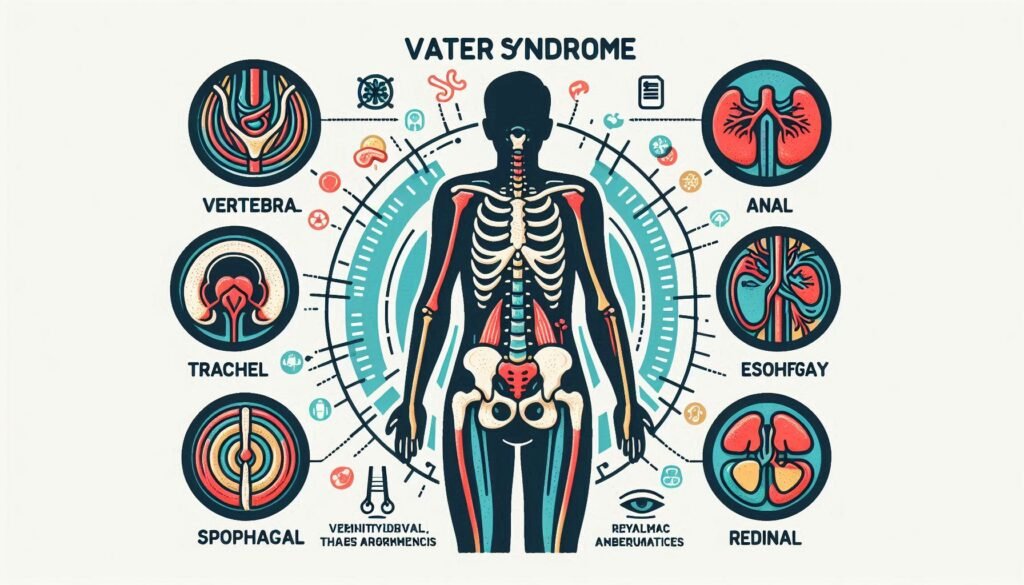
This guide will delve into the intricacies of VATER Syndrome, exploring its genetic roots, clinical features, and treatment options available today. By breaking down each component of the acronym—vertebral defects anal atresia, tracheoesophageal fistula, esophageal atresia, and radial dysplasia—we aim to provide clarity and support for loved ones facing this multifaceted condition.
Whether you are a parent seeking information or a medical professional wanting to enhance your knowledge base on VATER Syndrome, you’re in the right place. Let’s embark on this journey together!
The Genetic and Environmental Factors Behind VATER Syndrome
VATER Syndrome is a complex condition that arises from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Although the exact causes remain unclear, specific genes have been implicated in its development. Research suggests that mutations or variations in certain genes may disrupt normal embryonic growth.
“How Does Nager Syndrome Impact Facial Development?”
Environmental influences also play a role. Factors such as maternal diabetes, exposure to teratogens, and nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy can contribute to the risk of VATER Syndrome. These elements potentially interfere with fetal development, leading to the characteristic abnormalities.
Understanding these factors helps healthcare professionals assess risks for affected families. Genetic counseling can provide insight into potential hereditary patterns, while awareness of environmental triggers emphasizes the importance of prenatal care for expectant mothers. By recognizing both genetic and external influences, we advance our knowledge about VATER Syndrome’s origins and improve management strategies for those impacted by it.
Understanding the VATER Acronym: Breaking Down Each Component
VATER Syndrome is an acronym that stands for a group of congenital anomalies. Each letter represents a specific condition, shedding light on the complexities of this rare disorder.
“What Are The Signs of Nance-Horan Syndrome?”
The “V” in VATER refers to vertebral defects. These can range from missing or fused vertebrae to abnormalities in spinal structure, impacting mobility or posture.
“A” signifies anal atresia, a condition where the anus is malformed or absent. This issue requires immediate medical attention and often surgical intervention shortly after birth.
“TE” denotes tracheoesophageal fistula, an abnormal connection between the trachea and esophagus. This can lead to severe feeding difficulties and respiratory complications.
Lastly, “R” stands for radial dysplasia. It involves malformations of the forearm bones and hands, affecting dexterity and function.
Understanding each component helps in diagnosing and managing VATER Syndrome effectively. Each case presents unique challenges that require tailored approaches for care.
Vertebral Defects in VATER Syndrome: Types and Implications
Vertebral defects are a key component of VATER syndrome and can vary widely in severity. These abnormalities often involve the formation of vertebrae or their alignment.
Common types include hemivertebrae, which result in an incomplete formation of a vertebra. This condition can lead to scoliosis, affecting posture and overall spinal health. Other defects may present as fused vertebrae, limiting mobility and flexibility.
“Why Does Nephrotic Syndrome Cause Protein Loss?”
The implications of these defects can be significant. They may cause chronic pain or discomfort as children grow. In some cases, they affect lung function due to altered thoracic structure.
Early detection through imaging studies is crucial for management planning. Regular follow-ups with orthopedic specialists help monitor any changes over time, ensuring timely interventions when necessary. Understanding these issues empowers families to advocate for appropriate care and support throughout the child’s development journey.
Anal Atresia: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Anal atresia is a congenital condition where the anal opening is absent or blocked. This defect can vary in severity, impacting how waste is eliminated from the body. Symptoms often present shortly after birth and may include signs of intestinal distress.
Diagnosis typically occurs during a physical examination by healthcare professionals. Imaging studies, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, may also be utilized to assess the extent of the condition.
“How Does Nail-Patella Syndrome Affect Development?”
Treatment for anal atresia usually involves surgical intervention. The primary goal is to create a functional anus so that bowel movements can occur naturally. Depending on individual circumstances, additional surgeries might be necessary as the child grows.
Postoperative care focuses on monitoring recovery and managing potential complications like infection or bowel obstruction. Early intervention plays a crucial role in ensuring better long-term outcomes for affected children. Regular follow-ups with pediatric specialists are essential for ongoing support and management.
Tracheoesophageal Fistula: Causes and Surgical Interventions
Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a congenital anomaly where an abnormal connection forms between the trachea and esophagus. This condition often occurs alongside esophageal atresia, complicating feeding and breathing for affected infants.
The precise cause of TEF remains unclear, but genetic factors are suspected to play a role. Environmental influences during pregnancy may also contribute to its development. Early detection is crucial as it impacts immediate care strategies.
“What Causes Nasal Glioma Syndrome in Infants?”
Surgical intervention typically involves repairing the fistula and reconstructing any malformations in the esophagus. Surgeons work meticulously to restore normal anatomy, ensuring that both airways function correctly without obstruction or leakage.
Post-surgery care focuses on monitoring recovery and preventing complications such as aspiration pneumonia. Many children thrive with ongoing support from pediatric specialists who manage their unique healthcare needs effectively throughout their early years.
Esophageal Atresia: Impact on Feeding and Long-term Health
Esophageal atresia is a congenital condition where the esophagus fails to connect properly to the stomach. This anomaly significantly impacts feeding from birth, as infants cannot swallow normally.
Feeding challenges often require specialized interventions. Babies might need alternative feeding methods, such as gastric tubes or parenteral nutrition. Early management is crucial for their growth and development.
“Why Does Neurocutaneous Melanosis Syndrome Occur?”
Long-term health concerns may arise due to complications like reflux or strictures. These conditions can affect eating habits and nutritional intake throughout childhood.
Additionally, children with esophageal atresia may face respiratory issues caused by aspiration. Regular follow-ups are essential for monitoring potential complications and ensuring appropriate care strategies are implemented.
Parents should be prepared for ongoing assessments that help address any developmental delays related to feeding difficulties. A multidisciplinary approach involving pediatricians, gastroenterologists, and dietitians ensures comprehensive support tailored to each child’s needs.
Radial Dysplasia: Hand and Arm Abnormalities in VATER Syndrome
Radial dysplasia is a common feature in individuals with VATER Syndrome. This condition affects the radius bone in the forearm, leading to various hand and arm abnormalities.
In cases of radial dysplasia, children may have underdeveloped or missing bones. These changes can result in limited wrist movement and functional challenges. The severity varies widely among affected individuals.
“How Does Sleep Apnea Syndrome Affect Your Health?”
Some might experience difficulty grasping objects or holding utensils. Others may require assistive devices for daily activities. Early intervention is crucial for improving functionality and independence.
Surgical options are available to address severe deformities. Procedures can help correct alignment issues and improve overall range of motion.
Therapy often plays a significant role as well. Occupational therapy helps enhance motor skills through tailored exercises and adaptive strategies that empower children as they grow.
Associated Conditions: Beyond the Core VATER Components
While VATER Syndrome is characterized by its core components, several associated conditions can also arise. These additional complications may vary widely among individuals.
Some children with VATER Syndrome experience cardiac defects. Congenital heart issues often require careful monitoring and sometimes surgical intervention.
Other possible associations include renal anomalies. Kidney malformations can lead to urinary tract infections and other complications that necessitate ongoing care.
Hearing impairments are also reported in some cases, placing emphasis on early auditory screening for affected infants.
Additionally, spinal abnormalities might occur outside of the vertebral defects typically noted in VATER Syndrome. These could affect mobility or posture throughout life.
Recognizing these associated conditions is crucial for comprehensive management and tailored treatment plans aimed at improving quality of life for children with this syndrome.
Prenatal Diagnosis: Screening and Testing for VATER Syndrome
Prenatal diagnosis of VATER Syndrome plays a crucial role in managing the condition early. Expectant parents can benefit from advanced screening techniques during pregnancy.
Ultrasound is often the first step. It can identify physical anomalies such as vertebral defects or gastrointestinal malformations. These abnormalities may raise suspicion for VATER-related issues, prompting further investigation.
Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS) are genetic tests that provide insight into potential chromosomal abnormalities. While these tests do not directly diagnose VATER Syndrome, they help rule out other syndromes with overlapping features.
Counseling is vital following any abnormal findings. Healthcare providers can guide families on what to expect after birth, discussing possible interventions and support systems available.
Early detection allows for better planning and coordination of care post-delivery, improving outcomes for babies diagnosed with this complex syndrome.
Neonatal Care for Infants with VATER Syndrome
Neonatal care for infants with VATER Syndrome is crucial due to the range of potential complications. Each case can vary significantly, necessitating a tailored approach from healthcare providers.
These infants often require immediate assessment after birth. Monitoring vital signs and evaluating any visible anomalies are essential steps in the initial examination.
Feeding issues may arise, especially if esophageal atresia is present. Specialized feeding techniques or tube feeding might be necessary until surgical interventions can address these concerns.
Close collaboration between pediatricians, surgeons, and specialists ensures comprehensive care. Regular follow-ups help track development and health outcomes.
Parents play an integral role during this time. They should receive support and education about their child’s condition to navigate medical decisions effectively.
With appropriate neonatal management, many infants with VATER Syndrome go on to thrive as they grow older.
Surgical Interventions: Timing and Approaches for Various Defects
Surgical interventions for VATER Syndrome are often vital for improving quality of life. Timing is crucial as it can vary based on the specific defects present in each child.
For instance, repairs for anal atresia typically occur within the first few days of life. Early intervention helps prevent complications and supports optimal growth.
Tracheoesophageal fistula corrections usually take place shortly after birth to ensure safe feeding and breathing. These surgeries require a skilled surgical team familiar with pediatric conditions.
Esophageal atresia may also necessitate immediate surgery to reconnect or reconstruct the esophagus, which affects feeding directly.
Radial dysplasia treatment varies more widely. Some children may benefit from orthopedic procedures later in childhood, depending on their individual needs and developmental progress.
Each case demands a personalized approach that considers both medical necessity and family circumstances. Regular follow-ups post-surgery play an essential role in monitoring recovery and addressing any issues that arise.
Long-term Medical Management of VATER Syndrome
Long-term medical management of VATER Syndrome requires a multidisciplinary approach. This ensures that all aspects of the condition are addressed comprehensively. Regular follow-ups with pediatric specialists, including gastroenterologists and orthopedic surgeons, are essential.
Monitoring growth and development is critical for children affected by VATER Syndrome. Healthcare providers should track milestones closely to identify any delays early on. Nutritional assessments must also be part of routine care, as feeding issues can persist.
Psychosocial support plays a significant role in managing long-term outcomes. Families may benefit from counseling services to navigate emotional challenges associated with the syndrome.
Regular imaging studies may be necessary to assess structural defects over time, particularly for spinal or cardiac anomalies. Coordination between various healthcare professionals helps ensure that each child’s needs are met effectively while fostering an environment conducive to optimal health and well-being.
Developmental Challenges and Early Intervention Strategies
Children with VATER Syndrome may face various developmental challenges. These can include delays in motor skills, speech, and cognitive abilities. Early identification of these issues is crucial for effective intervention.
Early intervention strategies play a vital role in supporting development. Speech therapy can enhance communication skills while occupational therapy helps improve fine motor coordination. Physical therapy is essential for strengthening muscles and improving mobility.
Families should work closely with healthcare professionals to create individualized plans tailored to the child’s needs. Regular assessments ensure that progress is monitored, allowing adjustments as necessary.
Support groups also offer valuable resources and insights from other families facing similar experiences. Connecting with others provides emotional support and practical tips for navigating daily challenges associated with VATER Syndrome’s developmental hurdles. Engaging children through play-based learning can further foster growth in a nurturing environment.
Nutritional Considerations for Children with VATER Syndrome
Nutritional needs for children with VATER Syndrome can be quite specific. Due to conditions like esophageal atresia or tracheoesophageal fistula, many infants struggle with feeding issues. Specialized formulas may be necessary to ensure adequate nutrition.
Parents should work closely with dietitians familiar with VATER-related challenges. They can recommend the best feeding strategies and monitor growth patterns. Some children might benefit from thickened liquids to prevent aspiration.
As these kids grow, it’s essential to incorporate a balanced diet that supports their overall health and development. Focus on introducing various food textures gradually, keeping in mind any oral-motor difficulties they may have.
Regular follow-ups are crucial for tracking nutritional status and adjusting diets as needed. A proactive approach helps optimize health outcomes while addressing individual dietary requirements effectively.
The Psychosocial Impact of VATER Syndrome on Families
The diagnosis of VATER Syndrome can be overwhelming for families. Parents often face a whirlwind of emotions, including fear, uncertainty, and anxiety about their child’s future.
Caring for a child with VATER Syndrome may require frequent medical visits and interventions. This can create stress within the family unit as they navigate complex healthcare systems and treatment plans.
Siblings might experience feelings of jealousy or confusion when attention is diverted to the needs of the affected child. Open communication is vital in helping them understand the situation better.
Support networks play an essential role in coping with these challenges. Connecting with other families facing similar circumstances fosters a sense of community and shared understanding.
Mental health resources are crucial too; parents may benefit from counseling services to address emotional struggles that arise during this journey.
Educational Support for Children with VATER Syndrome
Children with VATER Syndrome often face unique educational challenges. Early identification of their needs is crucial for effective support. Tailored education plans can help address learning difficulties that may arise from physical and developmental differences.
Collaboration among educators, therapists, and families ensures a comprehensive approach to each child’s education. Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) are essential tools that outline specific goals and accommodations for children with VATER Syndrome.
Many students benefit from speech therapy to improve communication skills, which can be impacted by associated conditions like tracheoesophageal fistula or esophageal atresia. Occupational therapy also plays a vital role in developing fine motor skills necessary for classroom tasks.
Fostering an inclusive environment enhances social interactions among peers. Awareness initiatives within schools can promote understanding and empathy amongst classmates, creating a supportive community for children facing these challenges. Regular assessments will ensure ongoing adjustments in teaching strategies as the child grows.
Transitioning to Adult Care: Challenges and Solutions
Transitioning from pediatric to adult care presents unique challenges for individuals with VATER Syndrome. Young adults often feel overwhelmed by the shift in medical responsibility and may struggle to navigate their healthcare needs independently.
Many face difficulties understanding their complex medical history. This can lead to anxiety about managing ongoing treatments or surgeries that might be necessary as they age. It’s crucial for them to form a relationship with new healthcare providers who understand VATER Syndrome.
Support systems play an essential role during this transition. Family involvement is vital, as it provides emotional backing while encouraging independence. Additionally, resources like patient advocacy groups can offer guidance on navigating adult health services.
Developing a personalized care plan tailored to their specific needs helps bridge the gap between childhood and adulthood. Regular check-ins with caregivers ensure continuity of care and adapt strategies based on evolving health requirements throughout life stages.
Current Research and Future Treatments for VATER Syndrome
Current research on VATER Syndrome is making strides in understanding its complex nature. Scientists are exploring genetic markers associated with the condition, which could improve diagnosis and help identify at-risk babies before birth. Advanced imaging techniques are also being developed for better prenatal screening.
Treatment approaches are evolving as well. Researchers are investigating minimally invasive surgical procedures that may reduce recovery times and complications for infants with defects like tracheoesophageal fistula and anal atresia. These innovations aim to enhance the quality of life for affected children from an early age.
Furthermore, multidisciplinary care teams continue to refine management strategies tailored to individual needs. This team approach includes pediatricians, surgeons, nutritionists, and therapists who work together to provide comprehensive support throughout a child’s development.
As we look ahead, clinical trials focusing on innovative therapies promise new avenues for treatment options that could significantly improve outcomes for those living with VATER Syndrome. With ongoing research efforts paving the way forward, there is hope that advancements will lead not only to better treatments but also enhanced overall quality of life for individuals impacted by this condition.


