Eagle Syndrome is a condition that often flies under the radar, yet its impact on those who suffer from it can be significant. Named after Dr. James Eagles, who first described it in 1937, this syndrome arises from abnormalities related to the styloid process and surrounding structures. While some individuals may experience minimal symptoms, others face chronic pain and discomfort that can severely affect their quality of life.
As we delve deeper into Eagle Syndrome, we’ll explore its anatomy, causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and how to manage daily living with this condition. Whether you’re seeking clarity for yourself or a loved one or are simply curious about lesser-known medical conditions, understanding Eagle Syndrome is essential for better awareness and support. Let’s take flight into the details of this intriguing syndrome!
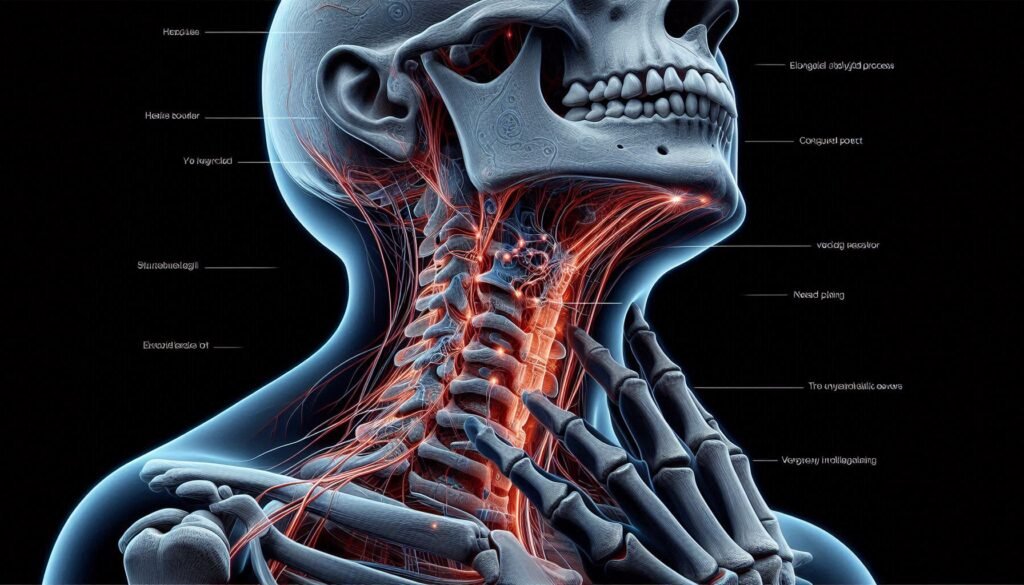
What is Eagle Syndrome?
Eagle Syndrome is a rare condition that arises from abnormalities associated with the styloid process, a slender bony projection located just below the ear. It can manifest in various ways, often leading to significant discomfort and pain.
Historically, this syndrome gained recognition in 1937 when Dr. James Eagles first documented it. He noted symptoms arising from elongated or calcified stylohyoid ligaments affecting nearby structures.
Patients may experience an array of symptoms due to nerve compression or irritation caused by these anatomical changes. These include facial pain, difficulty swallowing, and even issues like tinnitus. While it’s relatively uncommon, understanding Eagle Syndrome is crucial for diagnosis and effective management.
“How Does Kelley-Seegmiller Syndrome Impact Metabolism?”
Awareness of its existence can lead to better outcomes for those who suffer silently with this often-misunderstood condition.
Definition and Overview
Eagle Syndrome is a rare medical condition characterized by elongated styloid processes or calcified stylohyoid ligaments. These anatomical abnormalities can lead to various symptoms, primarily affecting the head and neck regions.
Patients often experience discomfort due to pressure on nearby nerves and structures. The condition can manifest in different ways, making diagnosis challenging. Symptoms may range from pain during swallowing to persistent earache.
“What Causes Keshan Disease Syndrome? Nutrition Guide”
The syndrome was first described in the 1930s by Dr. Eagle, who linked it to tonsillectomy patients experiencing unusual throat pain. Since then, awareness has grown about how this disorder impacts individuals beyond the initial context of surgery.
Understanding Eagle Syndrome requires knowledge of its underlying anatomy and symptomatology, which are critical for effective management and treatment options available today.
Historical Context
Eagle Syndrome was first documented in the 1930s by Dr. James Eagles, an American otolaryngologist. He identified a link between elongated styloid processes and various symptoms experienced by patients.
Initially, it was considered a rare condition. However, as medical imaging technology advanced, more cases were discovered. This led to increased awareness among healthcare professionals regarding its potential impact on quality of life.
“How Does Kawasaki Syndrome Affect Children?”
Throughout the years, researchers have delved deeper into understanding Eagle Syndrome. They sought to elucidate its anatomical variations and implications for treatment options.
The evolution of diagnostic techniques has played a significant role in shifting perceptions about this syndrome from obscurity to recognition within modern medicine. Today, it is acknowledged not just for its physical manifestations but also for its profound effects on individuals’ daily lives and well-being.
Anatomy and Pathophysiology
Eagle Syndrome primarily involves abnormalities of the styloid process and the associated structures. The styloid process is a slender bone extending from the temporal bone of the skull. In individuals with Eagle Syndrome, this bone can be elongated or malformed, leading to various symptoms.
Calcification of the stylohyoid ligament often occurs alongside these changes. This ligament connects the hyoid bone to the styloid process and its calcification can contribute to discomfort in related areas.
“What Causes Laron Syndrome? Growth Disorder Guide”
Anatomical variations play a crucial role as well. Some individuals may have naturally longer or thicker processes that predispose them to develop symptoms later in life. Understanding these anatomical details helps clarify how they relate to symptom severity and patient experience.
Styloid Process Abnormalities
Styloid process abnormalities are key factors in Eagle Syndrome. The styloid process is a slender bony projection located at the base of the skull, extending down from the temporal bone.
In individuals with Eagle Syndrome, this structure may be elongated or calcified. An unusually long styloid process can lead to discomfort and pain as it impinges on surrounding structures.
These variations can cause irritation of nearby nerves and tissues. Symptoms often arise when pressure affects critical areas such as the throat or neck.
“Why Does Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome Cause Self-Injury?”
Measurements indicate that a typical styloid process length ranges from 2 to 3 centimeters. Lengths exceeding this range may contribute significantly to clinical symptoms associated with Eagle Syndrome, emphasizing the need for thorough evaluation in affected patients.
Stylohyoid Ligament Calcification
Stylohyoid ligament calcification is a key aspect of Eagle Syndrome. This condition occurs when the stylohyoid ligament, which connects the styloid process of the skull to the hyoid bone in the neck, undergoes pathological changes.
Calcification can lead to an increase in stiffness and reduced flexibility of this ligament. As a result, it may exert pressure on nearby structures. Patients often experience discomfort or pain due to this added tension.
“How Does Li-Fraumeni Syndrome Increase Cancer Risk?”
Symptoms associated with calcification include facial and neck pain along with swallowing difficulties. The degree of calcification varies among individuals, influencing both symptom severity and treatment options.
Imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans are commonly used for diagnosis. Detecting these changes early can help provide appropriate care and management strategies for those affected by Eagle Syndrome.
Anatomical Variations
Anatomical variations in the styloid process and surrounding structures can significantly influence the presentation of Eagle Syndrome. These variations may include differences in length, shape, or orientation of the styloid process.
A longer-than-average styloid process is often associated with increased discomfort. The relationship between this structure and nearby nerves may lead to a higher likelihood of symptoms manifesting.
“What Are The Early Signs of Leigh Syndrome?”
Additionally, some individuals might have an unusual configuration of the hyoid bone or other cervical structures. This can further complicate diagnosis and management since these atypical anatomies can mimic other conditions.
Understanding these anatomical nuances is essential for healthcare professionals when evaluating patients suspected of having Eagle Syndrome. Accurate identification helps guide effective treatment strategies tailored to each patient’s unique anatomy.
Causes and Risk Factors
Eagle Syndrome can arise from various causes and risk factors that contribute to its development. Traumatic events, such as a neck injury or surgery, may lead to changes in the styloid process or surrounding structures. These incidents often spark inflammation or irritation, leading to symptoms.
Age and gender also play significant roles. Studies indicate that individuals over 30 years old are more prone to this syndrome. Additionally, women seem to experience Eagle Syndrome more frequently than men, though the reasons for this discrepancy remain unclear.
“Why Does Lhermitte-Duclos Syndrome Affect The Cerebellum?”
Genetic predisposition could influence susceptibility as well. In some cases, family history may reveal patterns of similar symptoms among relatives. Understanding these underlying factors helps in identifying at-risk populations and tailoring preventive measures effectively.
Traumatic Events
Traumatic events can play a significant role in the development of Eagle Syndrome. These incidents often involve direct injury to the neck or head region, which may lead to abnormalities in the styloid process.
Such trauma can occur from accidents, falls, or sports-related injuries. The impact might cause elongation of the styloid process or calcification of surrounding ligaments.
When these structures are altered, they can press against nearby nerves and tissues. This pressure contributes to various symptoms associated with Eagle Syndrome.
Interestingly, not everyone who experiences neck trauma will develop this condition. Individual anatomy and genetic factors also influence whether one is affected following an injury.
Understanding this link between traumatic events and Eagle Syndrome helps in identifying at-risk individuals for early diagnosis and treatment options.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age plays a significant role in the prevalence of Eagle Syndrome. Most commonly, individuals between the ages of 30 and 60 are diagnosed. This demographic is often more susceptible to anatomical changes that contribute to symptoms.
Gender also influences incidence rates. Research indicates that women are diagnosed with Eagle Syndrome more frequently than men. Hormonal factors or differences in anatomy may explain this disparity.
As age progresses, calcification of the stylohyoid ligament tends to increase, exacerbating symptoms for some individuals. The combination of aging and gender can affect how patients experience pain and other related issues.
Awareness of these considerations can help healthcare providers identify at-risk populations sooner. Early detection leads to better management strategies tailored to individual needs based on age and gender dynamics.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of Eagle Syndrome. While not everyone with a family history will experience this condition, certain hereditary factors can increase susceptibility.
Research indicates that specific genetic markers may influence bone density and growth patterns, which could lead to abnormalities in the styloid process or calcification of the stylohyoid ligament.
Families affected by Eagle Syndrome often report similar symptoms across generations. This suggests an inherited component that deserves further investigation.
Understanding genetic links is crucial for identifying at-risk individuals early on. Genetic counseling may offer valuable insights for those concerned about their family history related to this syndrome.
By exploring these genetic connections, healthcare providers can tailor preventive measures and treatments more effectively for patients who might be genetically predisposed to developing Eagle Syndrome.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Eagle Syndrome can manifest through a variety of symptoms that significantly impact daily life. One common complaint is facial and neck pain, often described as sharp or throbbing. This discomfort can radiate, making it difficult for patients to find relief.
Swallowing difficulties are another hallmark symptom. Patients may experience sensations of obstruction or discomfort in the throat, leading to anxiety during meals.
Ear-related issues such as pain and tinnitus frequently accompany Eagle Syndrome. The ear pain may feel like pressure or fullness, while tinnitus presents as ringing or buzzing sounds that persist despite external noise.
Headaches and dizziness are also prevalent among those affected by this condition. These symptoms can create challenges in maintaining focus and balance throughout the day. Each patient’s experience varies widely, underscoring the complexity of diagnosing this syndrome effectively.
Facial and Neck Pain
Facial and neck pain are common complaints among individuals with Eagle Syndrome. This discomfort often arises due to the pressure exerted by elongated or calcified styloid processes on surrounding tissues.
Patients frequently describe a sharp, radiating pain that can extend from the jawline to the base of the skull. This pain may vary in intensity and is sometimes exacerbated by activities such as chewing or turning the head.
Inflammation in adjacent areas can contribute to muscle tension, leading to further discomfort. Many report that facial expressions trigger their symptoms, making everyday interactions challenging.
While this type of pain can be distressing, recognizing its connection to Eagle Syndrome is crucial for effective management. Understanding these sensations allows patients and healthcare providers alike to explore appropriate treatment options tailored specifically for relief.
Swallowing Difficulties
Swallowing difficulties, known medically as dysphagia, are a common symptom of Eagle Syndrome. Patients often report discomfort and pain during the act of swallowing. This can lead to anxiety around eating and drinking.
The elongated styloid process or calcified ligaments may compress nearby structures such as the throat or esophagus. This pressure results in sensations of tightness or obstruction when food passes down.
Individuals may also experience a sensation that food is stuck in their throat. This feeling can be distressing and contribute to avoidance behaviors regarding meals.
Furthermore, these challenges might lead to changes in diet, with some opting for softer foods that require less effort to swallow. The impact on nutrition should not be overlooked; proper dietary adjustments are essential for maintaining health while managing symptoms associated with Eagle Syndrome.
Ear Pain and Tinnitus
Ear pain and tinnitus are common symptoms associated with Eagle Syndrome. Patients often describe the ear pain as sharp, throbbing, or aching. This discomfort can stem from pressure exerted by elongated styloid processes.
Tinnitus, characterized by a ringing or buzzing sound in the ears, frequently accompanies this condition. The abnormal structures may irritate surrounding nerves, leading to auditory disturbances.
Many affected individuals report that their tinnitus fluctuates in intensity. Stress and fatigue can exacerbate these sensations.
Understanding the link between oral health and ear issues is crucial for effective management. Those experiencing persistent ear pain alongside other symptoms should consult healthcare professionals for proper evaluation and treatment options tailored to their needs.
Headaches and Dizziness
Headaches and dizziness are common complaints among individuals with Eagle Syndrome. These symptoms can significantly affect daily activities.
The headaches may vary in intensity and often manifest as a dull ache or sharp pain around the temples, neck, or behind the eyes. This discomfort is frequently linked to irritation of nearby nerves caused by elongated styloid processes.
Dizziness can occur simultaneously with headaches, leading to feelings of lightheadedness or unsteadiness. It may be exacerbated during certain movements, such as turning the head quickly.
Patients might experience episodes that range from mild vertigo to severe balance issues. This symptomatology can lead to anxiety and exacerbate discomfort overall.
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for effective management and addressing patient concerns during diagnosis. Recognition allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment options accordingly.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing Eagle Syndrome involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging techniques. A thorough physical examination is essential. Physicians assess the patient’s history, symptoms, and any potential triggers for discomfort.
Imaging plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis. X-rays can reveal abnormalities in the styloid process or calcifications of the stylohyoid ligament. CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional views that help visualize these structures more clearly.
Differential diagnosis is equally important to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as temporomandibular joint disorders or cervical spine issues. Collaboration among healthcare providers enhances accuracy in diagnosing this often-misunderstood syndrome.
Clear communication between patients and doctors about symptom onset and severity aids in tailoring effective treatment plans based on specific findings from diagnostic approaches.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination for Eagle Syndrome, the clinician will focus on specific areas of concern. A thorough assessment of the head and neck is essential. The physician palpates various structures to identify any abnormalities or tenderness.
An important component involves examining the tonsillar region, as pain in this area can be indicative of styloid process elongation. The clinician may also assess range of motion in the jaw and neck, looking for limitations that could suggest associated issues.
Neurological evaluations are often conducted to rule out other conditions affecting sensation or motor function. Observing how symptoms present during these tests helps narrow down potential diagnoses.
Listening carefully to patient-reported symptoms further guides the practitioner’s approach, leading them towards appropriate imaging studies if Eagle Syndrome remains suspected after initial findings.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosing Eagle Syndrome. Accurate visualization of the styloid process and surrounding structures is essential for effective assessment.
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) is often the preferred method due to its ability to provide detailed 3D images. This allows clinicians to measure the length of the styloid process and identify any calcifications in the stylohyoid ligament.
Panoramic radiography can also be useful, though it offers less detail. It provides a broader view of oral and maxillofacial anatomy but may miss subtle abnormalities associated with Eagle Syndrome.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) might be employed when soft tissue evaluation is necessary, especially if there’s suspicion of nerve involvement or other complications. Each imaging modality has its strengths, contributing valuable insights into this complex condition.
Differential Diagnosis of Eagle Syndrome
Differential diagnosis for Eagle Syndrome is crucial due to its overlapping symptoms with various conditions. Healthcare providers often consider temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders first, as they can present with similar facial and neck pain.
Another condition that mimics Eagle Syndrome is glossopharyngeal neuralgia. This disorder leads to severe throat pain and difficulty swallowing, further complicating the clinical picture.
Additionally, cervical spine issues may contribute to neck discomfort and headaches. These problems must be thoroughly evaluated to rule out other sources of pain.
In some cases, tumors or cysts in the head and neck region can also exhibit signs akin to those seen in Eagle Syndrome. Advanced imaging techniques help distinguish these possibilities from styloid process abnormalities effectively.
A comprehensive patient history combined with targeted examinations ensures accurate identification of this complex syndrome amid its differential diagnoses.
Eagle Syndrome Treatment Options
Eagle Syndrome treatment options vary depending on the severity of symptoms and underlying causes. Many patients initially benefit from conservative management strategies. These can include pain relief medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to reduce discomfort.
For those with persistent or severe symptoms, surgical interventions may be necessary. The most common procedure involves removing the elongated styloid process or calcified ligament. This surgery often alleviates pain and improves quality of life.
Minimally invasive procedures are also gaining traction in treating Eagle Syndrome. Techniques such as endoscopic surgery allow for reduced recovery time while effectively addressing symptom-causing structures.
Patients should work closely with healthcare providers to determine the best approach tailored to their needs. Regular follow-ups help monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed for optimal results.
Conservative Management
Conservative management for Eagle Syndrome focuses on alleviating symptoms without surgical intervention. This approach is often the first line of treatment, especially for those with mild to moderate discomfort.
Pain relief can be achieved through over-the-counter medications such as NSAIDs. These drugs help reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain.
Physical therapy may also play a significant role in conservative management. Targeted exercises can improve neck mobility and strengthen surrounding muscles, which may ease tension.
Patients are encouraged to adopt lifestyle modifications that minimize symptoms. Techniques like proper posture, stress reduction strategies, and avoiding certain movements can significantly impact overall comfort.
Additionally, heat or cold applications might offer localized relief. Warm compresses can soothe sore areas while ice packs might decrease swelling during flare-ups. Such methods allow individuals to manage their condition effectively without resorting to invasive procedures.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions for Eagle Syndrome are often considered when conservative management fails to relieve symptoms. The primary goal of surgery is to alleviate pain and discomfort caused by the elongated styloid process or calcified stylohyoid ligaments.
The most common surgical procedure involves the excision of the elongated styloid process. This operation can be performed through an intraoral approach, which minimizes external scarring, or via a neck incision for better visualization in complex cases.
Patients typically experience significant symptom relief post-surgery. However, like any surgical procedure, risks such as infection or nerve damage exist.
Surgeons usually assess each case individually before recommending surgery. A thorough evaluation helps ensure that patients understand their options and potential outcomes related to this intervention.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures for Eagle Syndrome focus on alleviating symptoms while reducing recovery time. These techniques often involve smaller incisions and advanced imaging, allowing for precise interventions.
One common approach is the endoscopic excision of the elongated styloid process. This method uses a tiny camera and specialized instruments to remove excess bone without significant tissue damage.
Another option is radiofrequency ablation, which targets abnormal nerve pathways causing pain. By disrupting these signals, patients may experience reduced discomfort with minimal downtime.
These procedures can lead to quicker healing and less postoperative pain compared to traditional surgeries. Patients often appreciate the lower risk of complications associated with larger surgical approaches, making them a favorable choice in managing Eagle Syndrome effectively.
Living with Eagle Syndrome
Living with Eagle Syndrome can be challenging, but there are strategies to help manage the condition. Pain management is crucial. Over-the-counter medications or prescription pain relievers may provide relief for many sufferers.
Incorporating gentle exercises and physical therapy into your routine can also alleviate discomfort. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, such as yoga or meditation, might further enhance well-being.
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role too. Maintaining good hydration and eating smaller meals can ease swallowing difficulties. Avoiding certain foods that trigger symptoms is essential.
The psychological impact of chronic pain shouldn’t be overlooked. Support groups and counseling can offer emotional assistance and coping strategies for those dealing with this syndrome’s effects on daily life. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges fosters a sense of community and understanding among individuals navigating Eagle Syndrome together.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain associated with Eagle Syndrome requires a multifaceted approach. Patients often benefit from over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen to alleviate discomfort.
In addition, physical therapy can play a crucial role. Targeted exercises may help strengthen neck muscles and improve mobility. Gentle stretches can also reduce tension in the affected areas.
Alternative therapies are worth exploring too. Acupuncture has shown promise for some individuals, providing relief without medication side effects. Mindfulness practices like meditation and yoga can further aid in managing stress levels and promoting relaxation.
Patients should work closely with healthcare providers to develop customized strategies tailored to their specific symptoms and needs. Regular follow-ups ensure that pain management plans remain effective as circumstances change over time.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with Eagle Syndrome. One effective strategy is to incorporate gentle exercises that focus on neck mobility. Stretching routines may help alleviate tension and reduce pain.
Dietary changes are also beneficial. Consuming soft foods can lessen discomfort during swallowing, while staying hydrated aids in overall health. Avoiding irritants such as alcohol and caffeine may further minimize symptoms.
Stress management techniques play a crucial role too. Practices like mindfulness meditation or yoga can enhance relaxation and decrease muscle tension around the affected areas.
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers ensure ongoing monitoring of symptoms and adjustments to treatment plans as needed. Building a support network, whether through friends or online communities, provides emotional comfort and shared experiences that resonate deeply with those facing similar challenges.
Psychological Impact
Living with Eagle Syndrome can be challenging not just physically, but also psychologically. The persistent pain and discomfort often lead to emotional distress.
Many individuals experience anxiety about their symptoms, fearing a serious underlying condition. This worry can exacerbate feelings of helplessness and frustration.
Social interactions may suffer as well. Patients might avoid gatherings or activities that could trigger pain episodes, leading to isolation.
Additionally, chronic conditions like Eagle Syndrome can contribute to depression over time. Patients may struggle with the unpredictability of their symptoms, impacting daily life and relationships.
Coping strategies are essential for mental well-being. Support groups can provide a network of understanding individuals who share similar experiences. Professional counseling may also help in managing the emotional challenges associated with this syndrome.
Eagle Syndrome Complications and Prognosis
Eagle Syndrome can lead to various complications if left untreated. Patients may experience chronic pain due to nerve compression from elongated styloid processes or calcified ligaments. This discomfort can significantly impact daily activities.
In some cases, vascular issues may arise. The styloid process’s proximity to major blood vessels can cause complications such as carotid artery compression, leading to serious health risks.
The long-term outlook for individuals with Eagle Syndrome varies. Some patients find relief through conservative management, while others require surgical intervention for lasting results. Recurrence rates after surgery generally remain low but are not negligible.
Emotional and psychological impacts shouldn’t be overlooked either. Chronic pain conditions often affect mental well-being, creating a need for comprehensive care that addresses both physical and emotional aspects of the syndrome.
Potential Complications
Eagle Syndrome can lead to several complications if left untreated. One significant concern is chronic pain, which often stems from nerve compression due to elongated styloid processes or calcified ligaments.
Patients may also experience difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia. This complication can result in nutritional challenges and increased risk of aspiration, where food enters the airway.
In some cases, individuals with Eagle Syndrome develop headaches that are severe and persistent. These migraines can interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
Additionally, there’s a potential for psychological impacts. Chronic pain and discomfort may lead to anxiety or depression, affecting emotional well-being.
Awareness of these complications is essential for effective management and treatment planning. Early intervention could help mitigate these risks significantly.
Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for individuals with Eagle Syndrome varies significantly. Many people experience chronic pain and discomfort, which can impact their quality of life. However, effective management strategies can help alleviate symptoms.
With appropriate treatment, some patients find significant relief and return to normal activities. Surgical interventions often lead to lasting improvements in symptom severity.
On the other hand, a subset of patients may continue to face challenges despite treatment efforts. Ongoing monitoring is essential for these individuals.
Additionally, emotional support plays a crucial role in managing the psychological aspects of living with this syndrome. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers are advisable to adjust treatments as needed.
Understanding that each case is unique helps set realistic expectations for those affected by Eagle Syndrome. This awareness fosters proactive engagement in one’s care journey.
Recurrence Rates
Recurrence rates for Eagle Syndrome can vary significantly among individuals. While some patients may experience persistent symptoms even after treatment, others might find considerable relief.
The likelihood of recurrence often hinges on the type of intervention employed. Surgical methods tend to offer a more permanent solution compared to conservative management strategies, which may lead to symptom flare-ups over time.
Factors such as anatomical variations and individual pain thresholds also play a role in how frequently symptoms resurface. Some studies suggest that those with significant styloid process elongation are at higher risk for reoccurrence.
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring any changes post-treatment. Understanding the potential for recurrence helps patients manage expectations and stay informed about their condition’s trajectory.
Research and Advancements
Recent studies have shed light on Eagle Syndrome, revealing new insights into its mechanisms and potential treatments. Researchers are investigating the role of inflammation in symptom development, aiming to understand how it may contribute to pain and discomfort.
Emerging diagnostic tools like 3D imaging technology enhance the accuracy of identifying styloid process abnormalities. These methods provide detailed anatomical views that improve diagnosis rates significantly.
Novel treatment approaches include targeted therapies aimed at alleviating symptoms without invasive procedures. For example, some researchers are exploring physical therapy techniques specifically designed for those suffering from Eagle Syndrome.
These advancements highlight a growing recognition of this condition within the medical community. As awareness increases, patients can expect better management options and improved outcomes in their care journey.
Eagle Syndrome Current Studies
Current research on Eagle Syndrome focuses on understanding its underlying mechanisms and improving diagnostic accuracy. Recent studies are delving into the relationship between styloid process elongation and specific symptoms, shedding light on how anatomical variations can influence patient experiences.
Researchers are also investigating the prevalence of this condition in different populations. Notably, they aim to identify genetic markers that may predispose individuals to develop Eagle Syndrome.
Advancements in imaging techniques have made it easier for clinicians to visualize detailed structures around the styloid process. This helps differentiate Eagle Syndrome from other conditions presenting similar symptoms.
Additionally, innovative therapeutic approaches are being explored. These include targeted pain management strategies that could provide relief without invasive procedures. As these studies progress, they hold promise for enhancing patient care and outcomes related to Eagle Syndrome.
Emerging Diagnostic Tools
Recent advancements in imaging technology are revolutionizing the diagnosis of Eagle Syndrome. Techniques such as 3D cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) provide enhanced visualization of the styloid process and surrounding structures. This detailed imagery aids physicians in identifying abnormalities that traditional X-rays may miss.
Additionally, ultrasound is gaining traction as a non-invasive diagnostic tool. It allows for real-time assessment of the stylohyoid ligament and potential calcifications without exposing patients to radiation.
Emerging biomarker research also shows promise. Identifying specific markers associated with inflammation could lead to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment approaches.
These innovations reflect a growing understanding of Eagle Syndrome, paving the way for improved patient outcomes through early detection and targeted management strategies. As research continues, we can expect even more sophisticated tools to emerge in clinical practice.
Novel Treatment Approaches
Eagle Syndrome continues to be a subject of interest and research within the medical community. As new studies emerge, they shed light on innovative treatment approaches that can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Researchers are exploring various techniques aimed at minimizing discomfort and improving quality of life for those affected by Eagle Syndrome. One such advancement involves the use of targeted therapies that focus on pain management while addressing the underlying anatomical issues associated with styloid process abnormalities. These methods seek not only to alleviate symptoms but also enhance overall well-being.
Additionally, advancements in minimally invasive surgical options have become promising alternatives for individuals who do not respond well to conservative treatments. Techniques like endoscopic surgery allow surgeons to remove excess tissue or bone without large incisions, which often leads to quicker recovery times and reduced post-operative complications.
Emerging diagnostic tools are also playing a pivotal role in how Eagle Syndrome is identified and treated. Enhanced imaging technologies provide clearer insights into individual cases, enabling healthcare providers to tailor their approach more effectively based on each patient’s unique condition.
As researchers continue their work in this field, it is hopeful that these novel treatment approaches will lead to better management strategies for Eagle Syndrome patients. The future holds promise as understanding deepens and resources expand, paving the way for improved care pathways tailored specifically for those living with this complex syndrome.


